Correlation between the chemical composition and the antimicrobial properties of seven samples of essential oils of endemic Thymes in Morocco against multi-resistant bacteria and pathogenic fungi
- PMID: 36164579
- PMCID: PMC9508645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.06.022
Correlation between the chemical composition and the antimicrobial properties of seven samples of essential oils of endemic Thymes in Morocco against multi-resistant bacteria and pathogenic fungi
Abstract
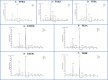
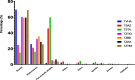
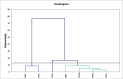
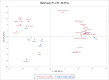
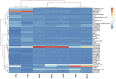
Thymus vulgaris, Thymus satureioides, and Thymus zygis are endemic Moroccan species that are intensively used due to their extensive medications and culinary properties. To enhance and preserve these overexploited species, the effect of provenance on the chemical composition of essential oils and antimicrobial activity against human pathogens were studied. Essential oils (EO) obtained by hydrodistillation from the flowering tops of thyme species were analyzed by GC-SM. The determination of minimum inhibitory (MIC), bactericidal (MBC), and fungicide (MFC) concentrations of EO were studied by microplate microdilution. The correlation between the chemical composition of EO and antimicrobial properties were evaluated using R software. The samples studied gave variable yields, ranging from 0.70 ± 0.03% to 4.12 ± 0.21%. The main constituents of Thymus vulgaris harvested from the municipality of El Hammam are carvacrol (68.8%), γ-terpinene (11.5%), and p-cymene (3.9%), while borneol (41.3% and 31.7%) and carvacrol (14.6% and 9.8%) are the most abundant in Thymus satureioides of the communes of Tata and Tigrigra respectively. For Thymus zygis, the results revealed the dominance of carvacrol (51.7% and 57.5%) for the municipalities of Tigrigra and Ain Aghbal, thymol (47.1% and 42.1%) for the municipalities of Bensmim and Timahdite respectively. These chemical profiles have similarities, but also reveal differences from the results given in the literature. In addition, the essential oils most active towards the microorganisms evaluated were those of Thymus vulgaris, followed by Thymus zygis and Thymus satureioides. These EO have very powerful MIC (MIC ⩽ 300 μg/ml) against Gram-negative bacteria, and in particular, concerning Enterobacters cloacae, Citrobacter koseri, and Acinetobacter baumannii. Thymus zygis EO is the most active on candidates compared to Thymus vulgaris and Thymus satureioides EO, except Candida dubliniensis which was inhibited by Thymus satureioides EO from the commune of Azrou with a MIC = 18.75 μg/ml. The correlation determined between the major components and MIC showed that phenols have the strongest positive effects on antimicrobial properties, followed by terpenes and non-aromatic alcohols. In addition, different sensitivities of pathogens to chemical families have been observed against Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter koseri, Candida parapsilosis, Staphylococcus aureus multiresistant, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Aspergillus niger. Our results support the idea that these oils could be very useful in flavoring, food preservation, as well as a source of antimicrobial agents of great power against multidrug-resistant strains.
Keywords: Borneol; Carvacrol; MBC; MFC; MIC; Multiresistant microorganisms; Thymol; Thymus satureioides; Thymus vulgaris; Thymus zygis.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, Robert P. 2007. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Vol. 456. Allured publishing corporation Carol Stream, IL
-
- AFNOR. 1972. « NF V05-113. Fruits, légumes et produits dérivés - Minéralisation des matières organiques - Méthode par incinération ». Afnor EDITIONS. 1972. https://www.boutique.afnor.org/fr-fr/norme/nf-v05113/fruits-legumes-et-p....
-
- AFNOR, 1985. « NF V03-402. Épices et aromates - Détermination de la teneur en eau - Méthode par entraînement. » Afnor EDITIONS. 1985. https://www.boutique.afnor.org/fr-fr/norme/nf-v03402/epices-et-aromates-...
-
- Aghraz A., Wanner J., Schmidt E., Aitdra L., Aitsidibrahim M., Tabanca N., Ali A., Nafis A., Hassani L., Markouk M., Jirovetz L., Larhsini M. Chemical composition, in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial and insecticidal activities of essential oil from cladanthus arabicus. J. Essen. Oil Bearing Plants. 2017;20(3):601–609. doi: 10.1080/0972060X.2017.1331143. - DOI
-
- Aicha N., Rachida T.C., El Abdelmalek M. Micropropagation of thymus satureioides coss. an endangered medicinal plant of Morocco. J. Agric. Technol. 2013;9(2):487–501.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

