The effect of calcium supplementation in people under 35 years old: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36164828
- PMCID: PMC9514846
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.79002
The effect of calcium supplementation in people under 35 years old: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: The effect of calcium supplementation on bone mineral accretion in people under 35 years old is inconclusive. To comprehensively summarize the evidence for the effect of calcium supplementation on bone mineral accretion in young populations (≤35 years).
Methods: This is a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Pubmed, Embase, ProQuest, CENTRAL, WHO Global Index Medicus, Clinical Trials.gov, WHO ICTRP, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Wanfang Data databases were systematically searched from database inception to April 25, 2021. Randomized clinical trials assessing the effects of calcium supplementation on bone mineral density (BMD) or bone mineral content (BMC) in people under 35 years old.
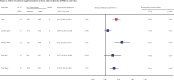
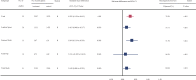
Results: This systematic review and meta-analysis identified 43 studies involving 7,382 subjects. Moderate certainty of evidence showed that calcium supplementation was associated with the accretion of BMD and BMC, especially on femoral neck (standardized mean difference [SMD] 0.627, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.338-0.915; SMD 0.364, 95% CI 0.134-0.595; respectively) and total body (SMD 0.330, 95% CI 0.163-0.496; SMD 0.149, 95% CI 0.006-0.291), also with a slight improvement effect on lumbar spine BMC (SMD 0.163, 95% CI 0.008-0.317), no effects on total hip BMD and BMC and lumbar spine BMD were observed. Very interestingly, subgroup analyses suggested that the improvement of bone at femoral neck was more pronounced in the peripeak bone mass (PBM) population (20-35 years) than the pre-PBM population (<20 years).
Conclusions: Our findings provided novel insights and evidence in calcium supplementation, which showed that calcium supplementation significantly improves bone mass, implying that preventive calcium supplementation before or around achieving PBM may be a shift in the window of intervention for osteoporosis.
Funding: This work was supported by Wenzhou Medical University grant [89219029].
Keywords: calcium; calcium supplementation; epidemiology; global health; none; osteoporosis; peak bone mass.
Plain language summary
Osteoporosis and bone fractures are common problems among older people, particularly older women. These conditions cause disability and reduce quality of life. Progressive loss of bone mineral density is usually the culprit. So far, strategies to prevent bone weakening with age have produced disappointing results. For example, taking calcium supplements in later life only slightly reduces the risk of osteoporosis or fracture. New approaches are needed. Bone mass increases gradually early in life and peaks and plateaus around 20-35 years of age. After that period, bone mass slowly declines. Some scientists suspect that increasing calcium intake during this period of peak bone mass may reduce osteoporosis or fracture risk later in life. A meta-analysis by Liu, Le et al. shows that boosting calcium intake in young adulthood strengthens bones. The researchers analyzed data from 43 randomized controlled trials that enrolled 7,382 participants. About half the studies looked at the effects of taking calcium supplements and the other half analyzed the effects of a high calcium diet. Boosting calcium intake in people younger than age 35 improved bone mineral density throughout the body. It also increased bone mineral density at the femoral neck, where most hip fractures occur. Calcium supplementation produced larger effects in individuals between the ages of 20 and 35 than in people younger than 20. Both high calcium diets and calcium supplements with doses less than 1000 mg/d boosted bone strength. Higher dose calcium supplements did not provide any extra benefits. The analysis suggests people should pay more attention to bone health during early adulthood. Large randomized clinical trials are needed to confirm the long-term benefits of boosting calcium intake during early adulthood. But if the results are validated, taking calcium supplements, or eating more calcium-rich foods between the ages of 20 and 35 may help individuals build healthier bones and prevent fractures and osteoporosis later in life.
© 2022, Liu, Le et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YL, SL, YL, HJ, BR, YH, XA, XS, XF, SW No competing interests declared
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utilization of DXA Bone Mineral Densitometry in Ontario: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(20):1-180. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074491 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combined calcium and vitamin D supplementation on osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Food Funct. 2020 Dec 1;11(12):10817-10827. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00787k. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 33237064
-
Effects of vitamin D supplementation on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Nov;6(11):847-858. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30293909
-
The effect of pregnancy vitamin D supplementation on offspring bone mineral density in childhood: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoporos Int. 2023 Jul;34(7):1269-1279. doi: 10.1007/s00198-023-06751-5. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Osteoporos Int. 2023. PMID: 37103591
-
Calcium supplementation for improving bone density in lactating women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Clin Nutr. 2020 Jul 1;112(1):48-56. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa103. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32401318
Cited by
-
Progress in Prevention and Treatment of Acute Bone Loss in Orthopedics.Int J Endocrinol. 2023 Nov 30;2023:9373043. doi: 10.1155/2023/9373043. eCollection 2023. Int J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 38077930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effects of Nutrients on Musculoskeletal Health in Gerontology: Understanding the Combined Impact of Macronutrients and Micronutrients.Nutrients. 2024 May 27;16(11):1640. doi: 10.3390/nu16111640. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892573 Free PMC article.
-
A Life-Stage Approach to Precision Nutrition: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 13;16(8):e66813. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66813. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39144414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Life Programming of Skeletal Health.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023 Aug;21(4):433-446. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00800-y. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023. PMID: 37335525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between arteriosclerosis index and lumbar bone mineral density in U.S adults: a cross-sectional study from the NHANES 2011-2018.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 1;11:1459062. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1459062. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39149583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bass SL, Naughton G, Saxon L, Iuliano-Burns S, Daly R, Briganti EM, Hume C, Nowson C. Exercise and calcium combined results in a greater osteogenic effect than either factor alone: a blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial in boys. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2007;22:458–464. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.061201. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

