Whole-Genome Sequencing for Resistance Prediction and Transmission Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Strains from Namibia
- PMID: 36165641
- PMCID: PMC9603870
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01586-22
Whole-Genome Sequencing for Resistance Prediction and Transmission Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Strains from Namibia
Abstract
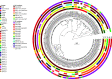
Namibia is among 30 countries with a high burden of tuberculosis (TB), with an estimated incidence of 460 per 100,000 population and around 800 new multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB cases per year. Still, data on the transmission and evolution of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (Mtbc) strains are not available. Whole-genome sequencing data of 136 rifampicin-resistant (RIFr) Mtbc strains obtained from 2016 to 2018 were used for phylogenetic classification, resistance prediction, and cluster analysis and linked with phenotypic drug susceptibility testing (pDST) data. Roughly 50% of the strains investigated were resistant to all first-line drugs. Furthermore, 13% of the MDR Mtbc strains were already pre-extensively drug resistant (pre-XDR). The cluster rates were high, at 74.6% among MDR and 85% among pre-XDR strains. A significant proportion of strains had borderline resistance-conferring mutations, e.g., inhA promoter mutations or rpoB L430P. Accordingly, 25% of the RIFr strains tested susceptible by pDST. Finally, we determined a potentially new bedaquiline resistance mutation (Rv0678 D88G) occurring in two independent clusters. High rates of resistance to first-line drugs in line with emerging pre-XDR and likely bedaquiline resistance linked with the ongoing recent transmission of MDR Mtbc clones underline the urgent need for the implementation of interventions that allow rapid diagnostics to break MDR TB transmission chains in the country. A borderline RIFr mutation in the dominant outbreak strain causing discrepancies between phenotypic and genotypic resistance testing results may require breakpoint adjustments but also may allow individualized regimens with high-dose treatment. IMPORTANCE The transmission of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) is a major problem for global TB control. Using genome sequencing, we showed that 13% of the multidrug-resistant (MDR) M. tuberculosis complex strains from Namibia are already pre-extensively drug resistant (pre-XDR), which is substantial in an African setting. Our data also indicate that the ongoing transmission of MDR and pre-XDR strains contributes significantly to the problem. In contrast to other settings with higher rates of drug resistance, we found a high proportion of strains having so-called borderline low-level resistance mutations, e.g., inhA promoter mutations or rpoB L430P. This led to the misclassification of 25% of the rifampicin-resistant strains as susceptible by phenotypic drug susceptibility testing. This observation potentially allows individualized regimens with high-dose treatment as a potential option for patients with few treatment options. We also found a potentially new bedaquiline resistance mutation in rv0678.
Keywords: Namibia; drug resistance; low-level resistance; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole-genome sequencing of clinical isolates from tuberculosis patients in India: real-world data indicates a high proportion of pre-XDR cases.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 May 2;12(5):e0277023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02770-23. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38597637 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of bedaquiline-resistant tuberculosis and of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with rpoB Ile491Phe mutation not detected by Xpert MTB/RIF in Mozambique: a retrospective observational study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Mar;24(3):297-307. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00498-X. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37956677
-
High fluoroquinolone resistance proportions among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis driven by dominant L2 Mycobacterium tuberculosis clones in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region.Genome Med. 2022 Aug 22;14(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01076-0. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 35989319 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance acquisition versus primary transmission in the presentation of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2022 Oct-Dec;11(4):343-348. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_187_22. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36510916 Review.
-
Epidemiology of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis among patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Jul;132:50-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.04.392. Epub 2023 Apr 16. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072053 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Whole genomic analysis uncovers high genetic diversity of rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in Botswana.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1535160. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1535160. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40008038 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Sierra Leone.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):e0240523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02405-23. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38289066 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: latest opinions on epidemiology, rapid diagnosis and management.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2024 May 1;30(3):217-228. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000001070. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38488133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. Meeting report of the WHO expert consultation on the definition of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/meeting-report-of-the-w....
-
- World Health Organization. 2019. Global tuberculosis report 2019. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/.
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. Global tuberculosis report 2020. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. Global tuberculosis report 2021. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/346387.
-
- Ministry of Health and Social Services. 2019. Namibia tuberculosis disease prevalence survey—report 2019. National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Programme, Windhoek, Namibia.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

