SID-4/NCK-1 is important for dsRNA import in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 36165710
- PMCID: PMC9635667
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac252
SID-4/NCK-1 is important for dsRNA import in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
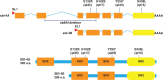
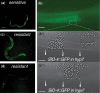
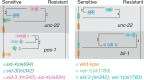
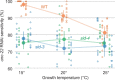
RNA interference is sequence-specific gene silencing triggered by double-stranded RNA. Systemic RNA interference is where double-stranded RNA, expressed or introduced into 1 cell, is transported to and initiates RNA interference in other cells. Systemic RNA interference is very efficient in Caenorhabditis elegans and genetic screens for systemic RNA interference-defective mutants have identified RNA transporters (SID-1, SID-2, and SID-5) and a signaling protein (SID-3). Here, we report that SID-4 is nck-1, a C. elegans NCK-like adaptor protein. sid-4 null mutations cause a weak, dose-sensitive, systemic RNA interference defect and can be effectively rescued by SID-4 expression in target tissues only, implying a role in double-stranded RNA import. SID-4 and SID-3 (ACK-1 kinase) homologs interact in mammals and insects, suggesting that they may function in a common signaling pathway; however, a sid-3; sid-4 double mutants showed additive resistance to RNA interference, suggesting that these proteins likely interact with other signaling pathways as well. A bioinformatic screen coupled to RNA interference sensitivity tests identified 23 additional signaling components with weak RNA interference-defective phenotypes. These observations suggest that environmental conditions may modulate systemic RNA interference efficacy, and indeed, sid-3 and sid-4 are required for growth temperature effects on systemic RNA interference silencing efficiency.
Keywords: C. elegans; NCK-1; RNAi; dsRNA.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tissue-specific overexpression of systemic RNA interference components limits lifespan in C. elegans.Gene. 2024 Feb 15;895:148014. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.148014. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37984536
-
SID-1 Domains Important for dsRNA Import in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Dec 4;7(12):3887-3899. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300308. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 29025917 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic RNA Interference Deficiency-1 (SID-1) Extracellular Domain Selectively Binds Long Double-stranded RNA and Is Required for RNA Transport by SID-1.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 31;290(31):18904-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.658864. Epub 2015 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26067272 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:95-100. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.060. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381285 Review.
-
Structural Perspective of the Double-Stranded RNA Transport Mechanism by SID-1 Family Proteins.Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(10):1610-1615. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b24-00419. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39358240 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated regulation of dopaminergic and epigenetic effectors of neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease models.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Feb 14;120(7):e2210712120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210712120. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36745808 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing by double-stranded RNA from C. elegans neurons reveals functional mosaicism of RNA interference.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 4;47(19):10059-10071. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz748. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31501873 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and unique mechanisms of RNAi-mediated antiviral immunity in C. elegans.Virology. 2025 Apr;605:110459. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2025.110459. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Virology. 2025. PMID: 40022946 Review.
-
Distinct pathways for export of silencing RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans systemic RNAi.iScience. 2023 Sep 28;26(10):108067. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108067. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37854694 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans transgenerational avoidance of P. fluorescens is mediated by the Pfs1 sRNA and vab-1.Sci Adv. 2025 Apr 25;11(17):eadt3850. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3850. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40267186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M, She H, Davis EM, Spicer CM, Kim L, Ren R, Le Beau MM, Li W.. Identification of Nck family genes, chromosomal localization, expression, and signaling specificity. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(39):25171–25178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
