Nicotinamide riboside kinase 1 protects against diet and age-induced pancreatic β-cell failure
- PMID: 36165811
- PMCID: PMC9557729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101605
Nicotinamide riboside kinase 1 protects against diet and age-induced pancreatic β-cell failure
Abstract
Objective: Disturbances in NAD+ metabolism have been described as a hallmark for multiple metabolic and age-related diseases, including type 2 diabetes. While alterations in pancreatic β-cell function are critical determinants of whole-body glucose homeostasis, the role of NAD+ metabolism in the endocrine pancreas remains poorly explored. Here, we aimed to evaluate the role of nicotinamide riboside (NR) metabolism in maintaining NAD+ levels and pancreatic β-cell function in pathophysiological conditions.
Methods: Whole body and pancreatic β-cell-specific NRK1 knockout (KO) mice were metabolically phenotyped in situations of high-fat feeding and aging. We also analyzed pancreatic β-cell function, β-cell mass and gene expression.
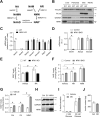
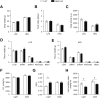
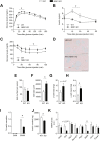
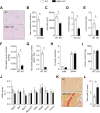
Results: We first demonstrate that NRK1, the essential enzyme for the utilization of NR, is abundantly expressed in pancreatic β-cells. While NR treatment did not alter glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic islets from young healthy mice, NRK1 knockout mice displayed glucose intolerance and compromised β-cells response to a glucose challenge upon high-fat feeding or aging. Interestingly, β cell dysfunction stemmed from the functional failure of other organs, such as liver and kidney, and the associated changes in circulating peptides and hormones, as mice lacking NRK1 exclusively in β-cells did not show altered glucose homeostasis.
Conclusions: This work unveils a new physiological role for NR metabolism in the maintenance of glucose tolerance and pancreatic β-cell function in high-fat feeding or aging conditions.
Keywords: Metabolic disease; NAD(+); Nicotinamide riboside; Nicotinamide riboside kinase 1 (NRK1).
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Leibson C.L., Williamson D.F., Melton 3rd L.J., Palumbo P.J., Smith S.A., Ransom J.E., et al. Temporal trends in BMI among adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(9):1584–1589. - PubMed
-
- Scheen A.J. Diabetes mellitus in the elderly: insulin resistance and/or impaired insulin secretion? Diabetes & Metabolism. 2005;(2) 31 Spec 5S27-S34. - PubMed
-
- Hawley J.A. Exercise as a therapeutic intervention for the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance. Disbetes Metabolism Research Review. 2004;20(5):383–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

