Concept Mapping to Identify Content for a Performance-Based Measure of Low Luminance Vision-Related Activities of Daily Living
- PMID: 36166222
- PMCID: PMC9526368
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.11.9.27
Concept Mapping to Identify Content for a Performance-Based Measure of Low Luminance Vision-Related Activities of Daily Living
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify low luminance activities of daily living (ADL) relevant to adults with vision impairment using a concept-mapping approach.
Methods: "Group concept mapping" was utilized to identify specific ADLs that persons with vision impairment find challenging under low light conditions. In the first "brainstorming" phase, 24 adults with vision impairment from a range of eye conditions (mean age = 73 years, SD = 14 years) and 26 international low vision experts (mean experience = 22, SD = 11 years) generated statements to the focus prompt, "Thinking as broadly as possible, generate a list of statements detailing specific day-to-day activities a person with vision impairment might find challenging under low light conditions, such as in a poorly lit room or outside at dusk." In the second phase, participants sorted activities by similarity and rated the importance of each activity. Multidimensional scaling and hierarchical cluster analysis were applied to produce concept maps showing clusters of prioritized activities.
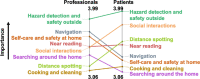
Results: One hundred thirteen unique ideas/activities were generated, rated and sorted. Eight clusters were identified (from highest to lowest importance): hazard detection and safety outside; social interactions; navigation; near reading; selfcare and safety at home; distance spotting; searching around the home; and cooking and cleaning.
Conclusions: The conceptual framework and low luminance ADLs identified (the most important being hazard detection and safety outside, and social interactions) provide a basis for developing a performance-based measure of low luminance visual function.
Translational relevance: A performance-based measure of low luminance vision-related ADLs is required for comprehensively and objectively assessing efficacy of eye treatments and low vision rehabilitation outcomes in adults with vision impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Wu Z, Guymer RH, Finger RP.. Low luminance deficit and night vision symptoms in intermediate age-related macular degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol . 2016; 100(3): 395–398. - PubMed
-
- Bierings R, van Sonderen FLP, Jansonius NM.. Visual complaints of patients with glaucoma and controls under optimal and extreme luminance conditions. Acta Ophthalmol . 2018; 96(3): 288–294. - PubMed
-
- Owsley C, McGwin G Jr, Scilley K, Kallies K. Development of a questionnaire to assess vision problems under low luminance in age-related maculopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci . 2006; 47(2): 528–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

