Prevalence of overweight and obesity and associated factors among people living with HIV attending a tertiary care clinic in Uganda
- PMID: 36167612
- PMCID: PMC9513878
- DOI: 10.1186/s40795-022-00604-w
Prevalence of overweight and obesity and associated factors among people living with HIV attending a tertiary care clinic in Uganda
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity are significantly increasing among people living with HIV (PLWH), contributing to the risk of major adverse cardio-metabolic events. However, little is known on its prevalence among PLWH in sub-Saharan Africa. In this study, we report the prevalence and factors associated with overweight and obesity among PLWH in a large tertiary HIV clinic in Kampala, Uganda.
Methods: A cross-sectional, retrospective review of electronic database of all PLWH that attended the Adult Infectious Diseases Institute clinic between November 2018 and April 2019 was conducted. Demographic, body mass index (BMI) [kg/m2] and clinical variables were extracted. Based on BMI, nutritional status was classified as undernutrition (< 18.5kg/m2), normal (≥ 18.5 < 25kg/m2), overweight (≥ 25 < 30kg/m2) and obesity (≥ 30kg/m2). Poisson regression analysis was performed to determine factors associated with overweight and obesity.
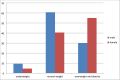
Results: Overall, 7,818 participants were included in the analysis, 64% (n = 4,976) were female, with a median age of 44 years (interquartile range (IQR): 36-51) and a median BMI of 24.2 (IQR: 21.2-28.1). The prevalence of overweight and obesity combined was 46% (55% female versus 30% male), obesity 18.2% (24.6% female versus 7.1% male) and overweight 27.8% (30.4% female versus 22.9% male). Factors associated with overweight and obesity were: Females (adjusted prevalence ratio [aPR]: 1. 8, 95%CI:1.69-1.87), age category 25-59 years (aPR: 1.9, 95%CI: 1.63-2.24) and ≥ 60 years (aPR: 1.8, 95%CI:1.49-2.12); duration on antiretroviral therapy (ART) for 6-10 years (aPR: 1.1, 95%CI:1.08-1.18), CD4 count 200-500 (aPR:0.08, 95%CI:0.01-0.15) and > 500 (aPR:0.46, 95%CI:0.39-0.54) and having at least one noncommunicable disease (NCD) (aPR: 1.1, 95%CI:1.07-1.18).
Conclusion: There is a high burden of overweight and obesity among PLWH in Uganda. Nutrition and weight management programs particularly targeting high risk groups such as females and persons with underlying NCDs should be integrated into HIV care.
Keywords: Body mass index; Non-communicable diseases; Obesity; Overweight.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Teshome MS, Gissa SB, Tefera BZ, Lema TB. Undernutrition and its predictors among people living with HIV/AIDS attending antiretroviral therapy clinic in Jimma University Specialized Hospital. Int J Nutr Metabolism. 2017;9(8):67–74.
-
- Takarinda KC, Mutasa-Apollo T, Madzima B, Nkomo B, Chigumira A, Banda M, et al. Malnutrition status and associated factors among HIV-positive patients enrolled in ART clinics in Zimbabwe. BMC Nutr. 2017;3(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40795-017-0132-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous