Early Low Pulse Pressure in VA-ECMO Is Associated with Acute Brain Injury
- PMID: 36167950
- PMCID: PMC10040467
- DOI: 10.1007/s12028-022-01607-y
Early Low Pulse Pressure in VA-ECMO Is Associated with Acute Brain Injury
Abstract
Background: Pulse pressure is a dynamic marker of cardiovascular function and is often impaired in patients on venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO). Pulsatile blood flow also serves as a regulator of vascular endothelium, and continuous-flow mechanical circulatory support can lead to endothelial dysfunction. We explored the impact of early low pulse pressure on occurrence of acute brain injury (ABI) in VA-ECMO.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of adults with VA-ECMO at a tertiary care center between July 2016 and January 2021. Patients underwent standardized multimodal neuromonitoring throughout ECMO support. ABI included intracranial hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, hypoxic ischemic brain injury, cerebral edema, seizure, and brain death. Blood pressures were recorded every 15 min. Low pulse pressure was defined as a median pulse pressure < 20 mm Hg in the first 12 h of ECMO. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to investigate the association between pulse pressure and ABI.
Results: We analyzed 5138 blood pressure measurements from 123 (median age 63; 63% male) VA-ECMO patients (54% peripheral; 46% central cannulation), of whom 41 (33%) experienced ABI. Individual ABIs were as follows: ischemic stroke (n = 18, 15%), hypoxic ischemic brain injury (n = 14, 11%), seizure (n = 8, 7%), intracranial hemorrhage (n = 7, 6%), cerebral edema (n = 7, 6%), and brain death (n = 2, 2%). Fifty-eight (47%) patients had low pulse pressure. In a multivariable model adjusting for preselected covariates, including cannulation strategy (central vs. peripheral), lactate on ECMO day 1, and left ventricle venting strategy, low pulse pressure was independently associated with ABI (adjusted odds ratio 2.57, 95% confidence interval 1.05-6.24). In a model with the same covariates, every 10-mm Hg decrease in pulse pressure was associated with 31% increased odds of ABI (95% confidence interval 1.01-1.68). In a sensitivity analysis model adjusting for systolic pressure, pulse pressure remained significantly associated with ABI.
Conclusions: Early low pulse pressure (< 20 mm Hg) was associated with ABI in VA-ECMO patients. Low pulse pressure may serve as a marker of ABI risk, which necessitates close neuromonitoring for early detection.
Keywords: Acute brain injury; Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; Neurological complication; Pulsatility; Pulse pressure.
© 2022. Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature and Neurocritical Care Society.
Figures
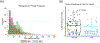



References
-
- Cho SM, Canner J, Chiarini G, et al. Modifiable risk factors and mortality from ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes in patients receiving venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Results from the extracorporeal life support organization registry. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(10):E897–E905. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004498 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lorusso R, Barili F, Mauro M Di, et al. In-Hospital Neurologic Complications in Adult Patients Undergoing Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Results from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(10):e964–e972. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001865 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ong CS, Etchill E, Dong J, et al. Standardized Noninvasive Multimodal Neuromonitoring, Diagnosis of Brain Injury and Neurological Outcomes in Patients on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support (preprint). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. Published online 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

