Design and synthesis of some new benzoylthioureido phenyl derivatives targeting carbonic anhydrase enzymes
- PMID: 36168122
- PMCID: PMC9542353
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2126463
Design and synthesis of some new benzoylthioureido phenyl derivatives targeting carbonic anhydrase enzymes
Abstract
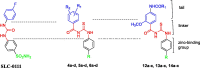
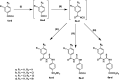
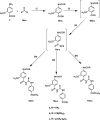
The present study aimed to develop potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs). The design of the target compounds was based on modifying the structure of the ureido-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitor SLC-0111. Six series of a substituted benzoylthioureido core were prepared featuring different zinc-binding groups; the conventional sulphamoyl group 4a-d and 12a-c, its bioisosteric carboxylic acid group 5a-d and 13a-c or the ethyl carboxylate group 6a-d and 14a-c as potential prodrugs. All compounds were assessed for their carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitory activity against a panel of four physiologically relevant human CA isoforms hCA I and hCA II, and hCA IX, and hCA XII. Compounds 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d, 5d, 12a, and 12c revealed significant inhibitory activity against hCA I that would highlight these compounds as promising drug candidates for the treatment of glaucoma.
Keywords: SLC-0111; Sulphonamides; benzoylthioureido derivatives; carbonic anhydrase.
Conflict of interest statement
C. T. Supuran is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry and he was not involved in the assessment, peer review, or decision-making process of this paper. The authors have no relevant affiliations of financial involvement with any organisation or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
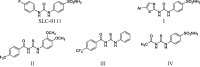
Similar articles
-
Exploring novel anticancer pyrazole benzenesulfonamides featuring tail approach strategy as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Dec 5;261:115805. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115805. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37748386
-
Novel 3-substituted coumarins as selective human carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors: Synthesis, biological and molecular dynamics analysis.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;209:112897. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112897. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33038795
-
Design and synthesis of benzothiazole-based SLC-0111 analogues as new inhibitors for the cancer-associated carbonic anhydrase isoforms IX and XII.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2635-2643. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2124409. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36146927 Free PMC article.
-
Click chemistry approaches for developing carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and their applications.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Jan 6;38(1):2166503. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2166503. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36637011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbonic anhydrases: Moiety appended derivatives, medicinal and pharmacological implications.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Nov 15;114:117933. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117933. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39378610 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of novel alkyl/benzyl (4-sulphamoylphenyl)carbamimidothioates as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2152811. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2152811. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36629134 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of specific carbonic anhydrase inhibitors via in situ click chemistry, phage-display and synthetic peptide libraries: comparison of the methods and structural study.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Nov 18;14(1):144-153. doi: 10.1039/d2md00330a. eCollection 2023 Jan 25. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36760748 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity of phthalimide-capped benzene sulphonamide derivatives.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2235089. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2235089. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37439360 Free PMC article.
-
Sulphonyl thiourea compounds containing pyrimidine as dual inhibitors of I, II, IX, and XII carbonic anhydrases and cancer cell lines: synthesis, characterization and in silico studies.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Dec 11. doi: 10.1039/d4md00816b. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39823041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassan MI, Shajee B, Waheed A, Ahmad F, Sly WS.. Structure, function and applications of carbonic anhydrase isozymes. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21(6):1570–1582. - PubMed
-
- Ghorai S, Pulya S, Ghosh K, Panda P, Ghosh B, Gayen S.. Structure-activity relationship of human carbonic anhydrase-II inhibitors: detailed insight for future development as anti-glaucoma agents. Bioorg Chem. 2020;95:103557. - PubMed
-
- Dar’in D, Kantin G, Kalinin S, Sharonova T, Bunev A, Ostapenko GI, Nocentini A, Sharoyko V, Supuran CT, Krasavin M.. Investigation of 3-sulfamoyl coumarins against cancer-related IX and XII isoforms of human carbonic anhydrase as well as cancer cells leads to the discovery of 2-oxo-2H-benzo [h] chromene-3-sulfonamide – a new caspase-activating proapoptotic agent. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;222:113589. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
