Dysbiosis and Migraine Headaches in Adults With Celiac Disease
- PMID: 36168375
- PMCID: PMC9506300
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.28346
Dysbiosis and Migraine Headaches in Adults With Celiac Disease
Abstract
One of the most significant illnesses associated with gluten is celiac disease, which encompasses many conditions. It is generally recognized that neurological manifestations can occur either at the time of the disease onset or as the illness continues to develop. One of the main clinical presentations of celiac disease is headache, either in the form of migraine or in an unspecific form. Migraine pathophysiology is intricate and still poorly understood. Several mechanisms involving the gut-brain axis have been proposed to explain this association. These include the interaction of chronic inflammation with inflammatory and vasoactive mediators, the modulation of the intestinal immune environment of the microbiota, and the dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. However, further research is required to fully comprehend the fundamental mechanisms and pathways at play. This review aims to give a narrative summary of the literature on celiac disease's neurological symptoms, particularly migraines, and to assess any potential associations to dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbiome.
Keywords: celiac disease and microbiota; celiac disease and migraine; gluten and microbiota; gut-brain axis; microbiota and migraine.
Copyright © 2022, Qasim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
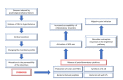
Figures
References
-
- Celiac disease symptom resolution: effectiveness of the gluten-free diet. Sansotta Naire, Amirikian Karine, Guandalini Guandalini, et al. https://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2018/01000/Celiac_Disease_Symptom.... J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr . 2018;66:48–52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
