Positive epigenetic regulation loop between AR and NSUN2 promotes prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 36169095
- PMCID: PMC9516604
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.1028
Positive epigenetic regulation loop between AR and NSUN2 promotes prostate cancer progression
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is a major type of cancer in man worldwide. Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) and the next-generation androgen receptor (AR) pathway inhibitors have acquired great success in treating PCa. However, patients treated with ADT or AR targeted therapy are inevitably developing into castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) or becoming drug resistance. The role of mRNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification in cancers is largely unknown. This study aimed to explore the role of the m5C methyltransferase NSUN2 in Prostate cancer (PCa).
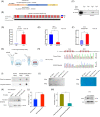
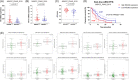
Methods: The expression of NSUN2 and its clinicopathological impact were evaluated in PCa cohorts. The effect of NSUN2 on the biological characteristics of PCa cells was investigated on the basis of gain-offunction and loss-of-function analyses. Subcutaneous models further uncovered the role of NSUN2 in tumor growth. Epi-transcriptome assays with RNA bisulfite sequencing (RNA-BisSeq) analysis and in vitro enzyme reaction assays were performed to validate the targeted effect of NSUN2 on AR. AR-binding sites in the NSUN2 promoter were investigated by ChIP and luciferase assays to uncover the interplay between NSUN2 and AR signaling. RIP-qPCR and EMSA methods were performed to confirm that YBX1 binds to AR m5 C sites.
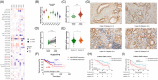
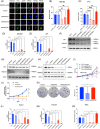
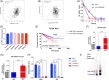
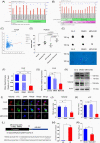
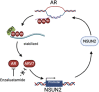
Results: NSUN2 is highly expressed in PCa and predicts poor outcome. NSUN2 plays roles as a PCa oncogene both in vitro and in vivo. Depletion of NSUN2 results in decreased expression and activities of AR, including AR-V7. Mechanistically, NSUN2 posttranscriptionally stabilized AR by cluster m5 C modification in a m5CYBX1-dependent manner. Strikingly, treatment with enzalutamide, an effective AR inhibitor, reduces NSUN2 expression and decreases the m5C modification level in prostate cancer cells. Finally, we found that AR transcriptionally regulates NSUN2.
Conclusion: NSUN2 stabilizes AR mRNA through cluster 5-methylcytosine modification and activates a positive feedback loop to promote prostate cancer.
Keywords: AR-V7; NSUN2; androgen receptor; castration-resistant prostate cancer; cluster; cytosine-5 methylation; prostate cancer.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IU1 and enzalutamide combination yields synergistic effects on castration-resistant prostate cancer.Prostate. 2023 Nov;83(15):1446-1457. doi: 10.1002/pros.24607. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Prostate. 2023. PMID: 37545197
-
Targeting the KIF4A/AR Axis to Reverse Endocrine Therapy Resistance in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 15;26(6):1516-1528. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0396. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31796514
-
Androgen receptor functions in castration-resistant prostate cancer and mechanisms of resistance to new agents targeting the androgen axis.Oncogene. 2014 May 29;33(22):2815-25. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.235. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23752196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Study using Malat1 Small Interfering RNA or Androgen Receptor Splicing Variant 7 Degradation Enhancer ASC-J9® to Suppress Enzalutamide-resistant Prostate Cancer Progression.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):835-844. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 May 18. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28528814 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the androgen receptor signaling pathway in advanced prostate cancer.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022 Jul 22;79(15):1224-1235. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxac105. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35390118 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel molecular mechanisms of immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: NSUN2-mediated increase of SOAT2 RNA methylation.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025 Jul;45(7):846-879. doi: 10.1002/cac2.70023. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40227950 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative multi-omics analysis and machine learning refine global histone modification features in prostate cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Mar 12;12:1557843. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1557843. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40144021 Free PMC article.
-
Isoimperatorin improves osteoporosis by increasing YBX1 expression to promote BGLAP m5C modification.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9734. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94215-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118929 Free PMC article.
-
NSUN2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by enhancing SKIL mRNA stabilization.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Mar;14(3):e1621. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1621. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38468490 Free PMC article.
-
The functions and mechanisms of RNA modification in prostate: Current status and future perspectives.Front Genet. 2024 May 10;15:1380746. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1380746. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38798700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115‐132. - PubMed
-
- Culp MB, Soerjomataram I, Efstathiou JA, Bray F, Jemal A. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2020;77(1):38‐52. - PubMed
-
- Gravis G, Fizazi K, Joly F, et al. Androgen‐deprivation therapy alone or with docetaxel in non‐castrate metastatic prostate cancer (GETUG‐AFU 15): a randomised, open‐label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(2):149‐158. - PubMed
-
- Fizazi K, Tran N, Fein L, et al. Abiraterone plus prednisone in metastatic, castration‐sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(4):352‐360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
