Development of an improved diagnostic nomogram for preoperative prediction of small cell neuroendocrine cancer of the cervix
- PMID: 36169239
- PMCID: PMC9733602
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20220368
Development of an improved diagnostic nomogram for preoperative prediction of small cell neuroendocrine cancer of the cervix
Abstract
Objectives: Accurate preoperative diagnosis of small cell neuroendocrine cancer of the cervix (SCNECC) is crucial for establishing the best treatment plan. This study aimed to develop an improved, non-invasive method for the preoperative diagnosis of SCNECC by integrating clinical, MR morphological, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) information.
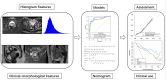
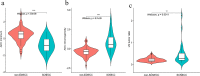
Methods: A total of 105 pathologically confirmed cervical cancer patients (35 SCNECC, 70 non-SCNECC) from multiple centres with complete clinical and MR records were included. Whole lesion histogram analysis of the ADC was performed. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to develop diagnostic models based on clinical, morphological, and histogram data. The predictive performance in terms of discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness of the different models was assessed. A nomogram for preoperatively discriminating SCNECC was developed from the combined model.
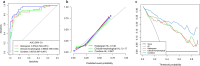
Results: In preoperative SCNECC diagnosis, the combined model, which had a diagnostic AUC (area under the curve) of 0.937 (95% CI: 0.887-0.987), outperformed the clinical-morphological model, which had an AUC of 0.869 (CI: 0.788-0.949), and the histogram model, which had an AUC of 0.872 (CI: 0.792-0.951). The calibration curve and decision curve analyses suggest that the combined model achieved good fitting and clinical utility.
Conclusions: Non-invasive preoperative diagnosis of SCNECC can be achieved with high accuracy by integrating clinical, MR morphological, and ADC histogram features. The nomogram derived from the combined model can provide an easy-to-use clinical preoperative diagnostic tool for SCNECC.
Advances in knowledge: It is clear that the therapeutic strategies for SCNECC are different from those for other pathological types of cervical cancer according to V 1.2021 of the NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology for cervical cancer. This research developed an improved, non-invasive method for the preoperative diagnosis of SCNECC by integrating clinical, MR morphological, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Multicenter Study on Preoperative Assessment of Lymphovascular Space Invasion in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer Based on Multimodal MR Radiomics.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Nov;58(5):1638-1648. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28676. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36929220
-
MR imaging of thymomas: a combined radiomics nomogram to predict histologic subtypes.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jan;31(1):447-457. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07074-3. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32700020
-
Single-Cell Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis Provide a New Approach for the Treatment of Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix.Neuroendocrinology. 2025;115(1):13-33. doi: 10.1159/000542833. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Neuroendocrinology. 2025. PMID: 39602898
-
Diagnostic value of four neuroendocrine markers in small cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the cervix: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 11;10(1):14975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72055-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32917946 Free PMC article.
-
Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix: From molecular basis to therapeutic advances.Biomed J. 2023 Oct;46(5):100633. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100633. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Biomed J. 2023. PMID: 37467967 Free PMC article. Review.

