Mucosal Interleukin-10 depletion in steroid-refractory Crohn's disease patients
- PMID: 36169258
- PMCID: PMC9514060
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.710
Mucosal Interleukin-10 depletion in steroid-refractory Crohn's disease patients
Abstract
Background: Previous studies suggested that Interleukin-10 (IL-10) depletion in Crohn's disease (CD) could predict outcome.
Aim: To determine IL-10 in blood and at different intestinal locations in patients with active CD and to assess its potential prognostic capacity to identify aggressive CD.
Methods: Twenty-three patients with CD were included. Ulcerative colitis (UC), infectious colitis and healthy individuals acted as controls. Serum and mucosal samples were taken at baseline and 1 month after steroid initiation in CD patients. Patients were classified according to steroid response. Control samples were obtained from different intestinal locations. IL-10 expression was measured with real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunofluorescence (intestine) and ELISA (serum, biopsy cultures' supernatants and tissue homogenates).
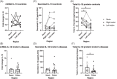
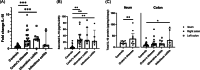
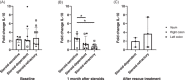
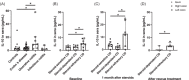
Results: CD and UC showed an increase in IL-10 messenger RNA (mRNA) versus controls (p < .0001) in mucosa, whereas IL-10 protein secretion was increased in all types of intestinal inflammation (p < .001). No differences in IL-10 mRNA were found in CD at baseline regarding steroid response, but levels decreased in non-responders versus responders (p = .027) and were restored with rescue therapy. Serum IL-10 was increased in steroid-refractory CD at baseline and after treatment.
Conclusions: Abnormal IL-10 levels in refractory patients in both mucosa and blood have physiopathological relevance and may have potential clinical applications.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; Interleukin-10; inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal compartmentalization; steroid resistance.
© 2022 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Paul G, Khare V, Gasche C. Inflamed gut mucosa: downstream of interleukin‐10. Eur J Clin Invest. 2012;41:95‐109. - PubMed
-
- De Souza HS, Fiocchi C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: current state of the art. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13:13‐27. - PubMed
-
- Bickston SJ, Cominelli F. Recombinant interleukin 10 for the treatment of active crohn's disease: lessons in biologic therapy. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1781‐1783. - PubMed
-
- Santaolalla R, Mañé J, Pedrosa E, et al. Apoptosis resistance of mucosal lymphocytes and IL‐10 deficiency in patients with steroid‐refractory Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:1490‐1500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

