Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease for Treatment of COVID-19: Covalent Inhibitors Structure-Activity Relationship Insights and Evolution Perspectives
- PMID: 36169610
- PMCID: PMC9528073
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01005
Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease for Treatment of COVID-19: Covalent Inhibitors Structure-Activity Relationship Insights and Evolution Perspectives
Abstract
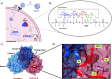
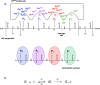
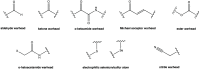
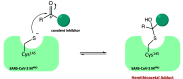
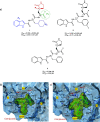
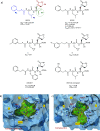
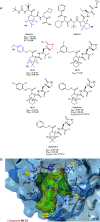
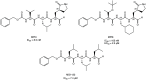
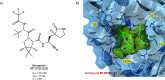
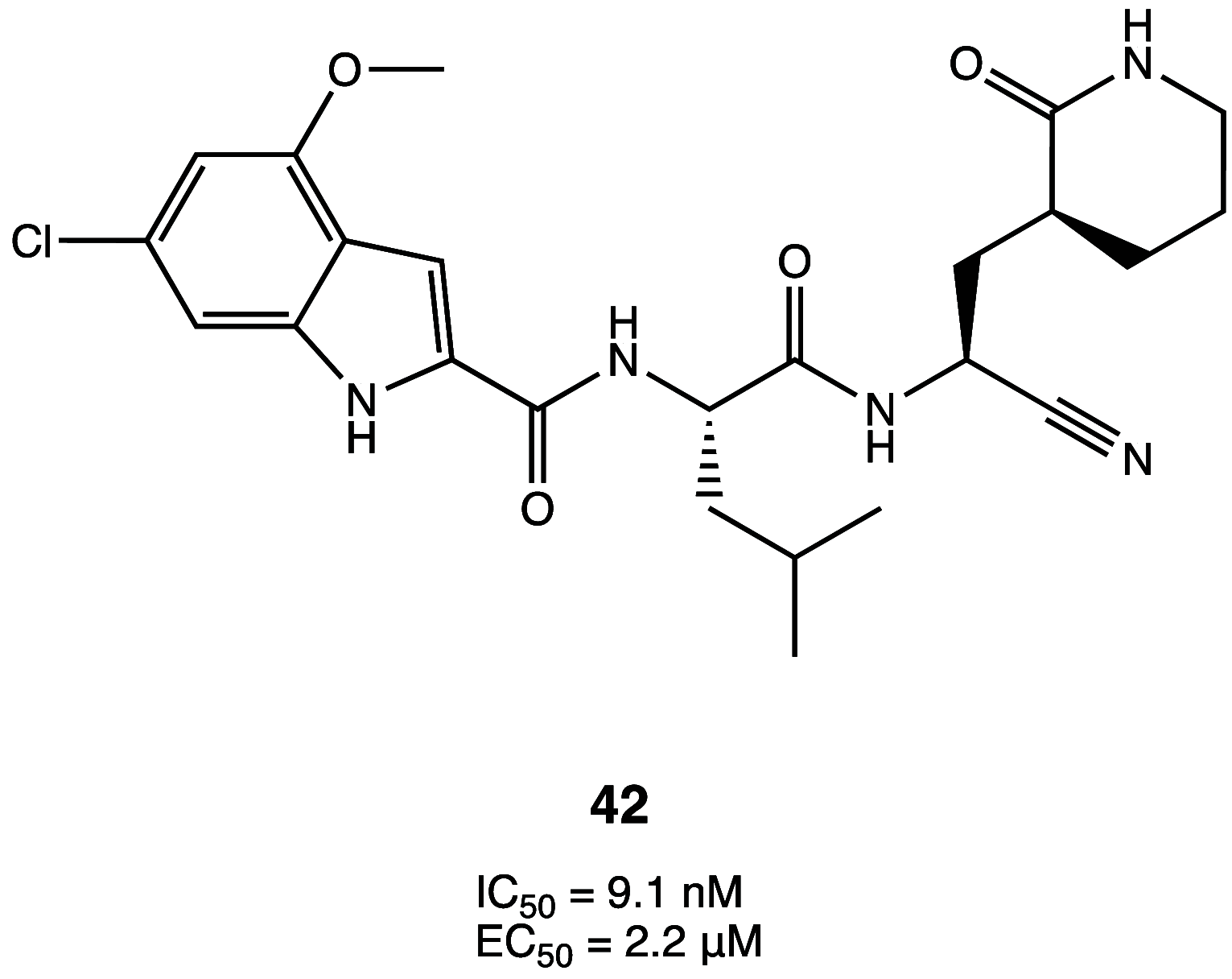
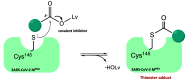
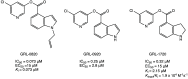
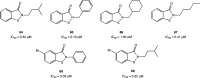
The viral main protease is one of the most attractive targets among all key enzymes involved in the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle. Covalent inhibition of the cysteine145 of SARS-CoV-2 MPRO with selective antiviral drugs will arrest the replication process of the virus without affecting human catalytic pathways. In this Perspective, we analyzed the in silico, in vitro, and in vivo data of the most representative examples of covalent SARS-CoV-2 MPRO inhibitors reported in the literature to date. In particular, the studied molecules were classified into eight different categories according to their reactive electrophilic warheads, highlighting the differences between their reversible/irreversible mechanism of inhibition. Furthermore, the analyses of the most recurrent pharmacophoric moieties and stereochemistry of chiral carbons were reported. The analyses of noncovalent and covalent in silico protocols, provided in this Perspective, would be useful for the scientific community to discover new and more efficient covalent SARS-CoV-2 MPRO inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
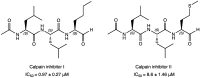
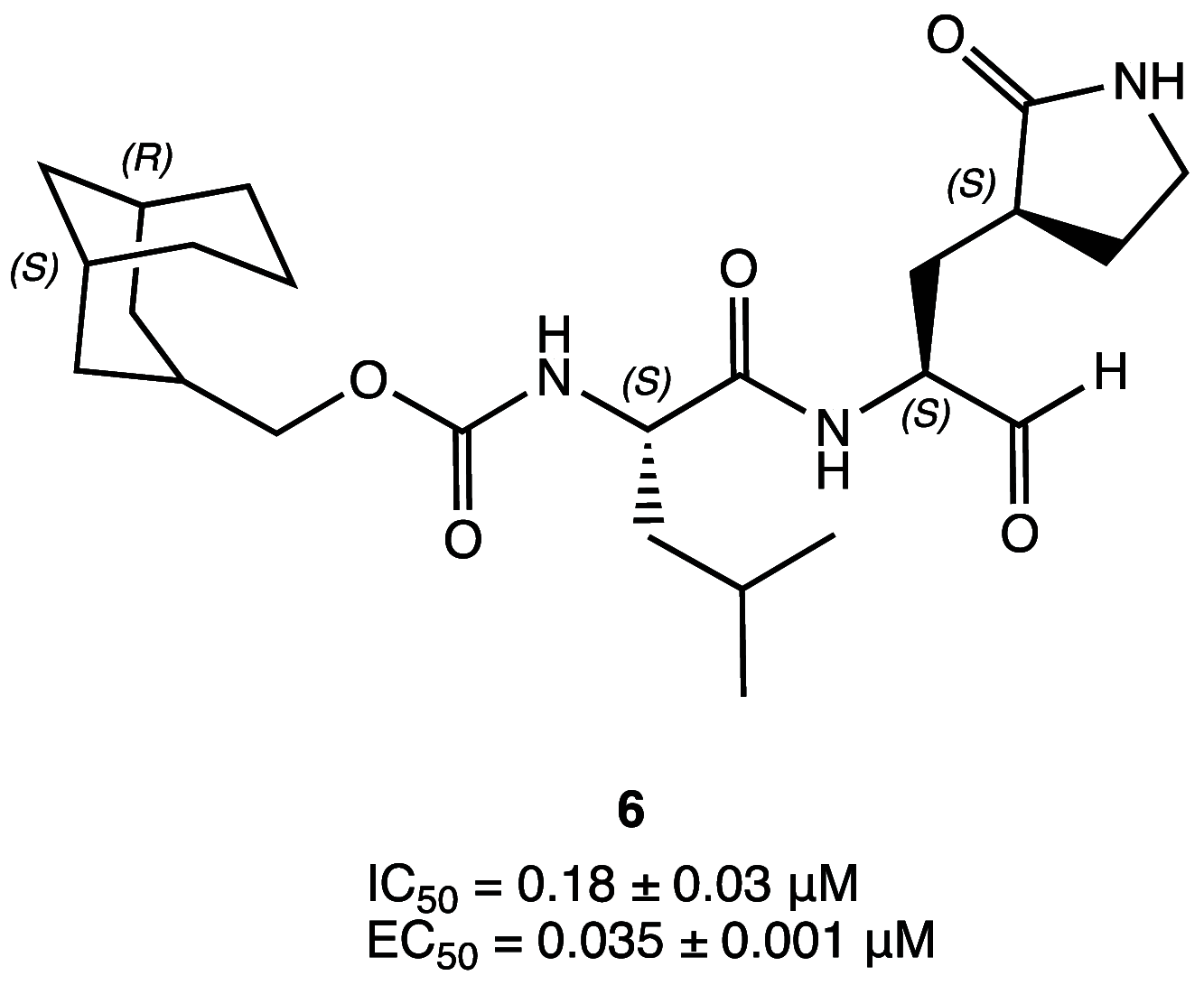
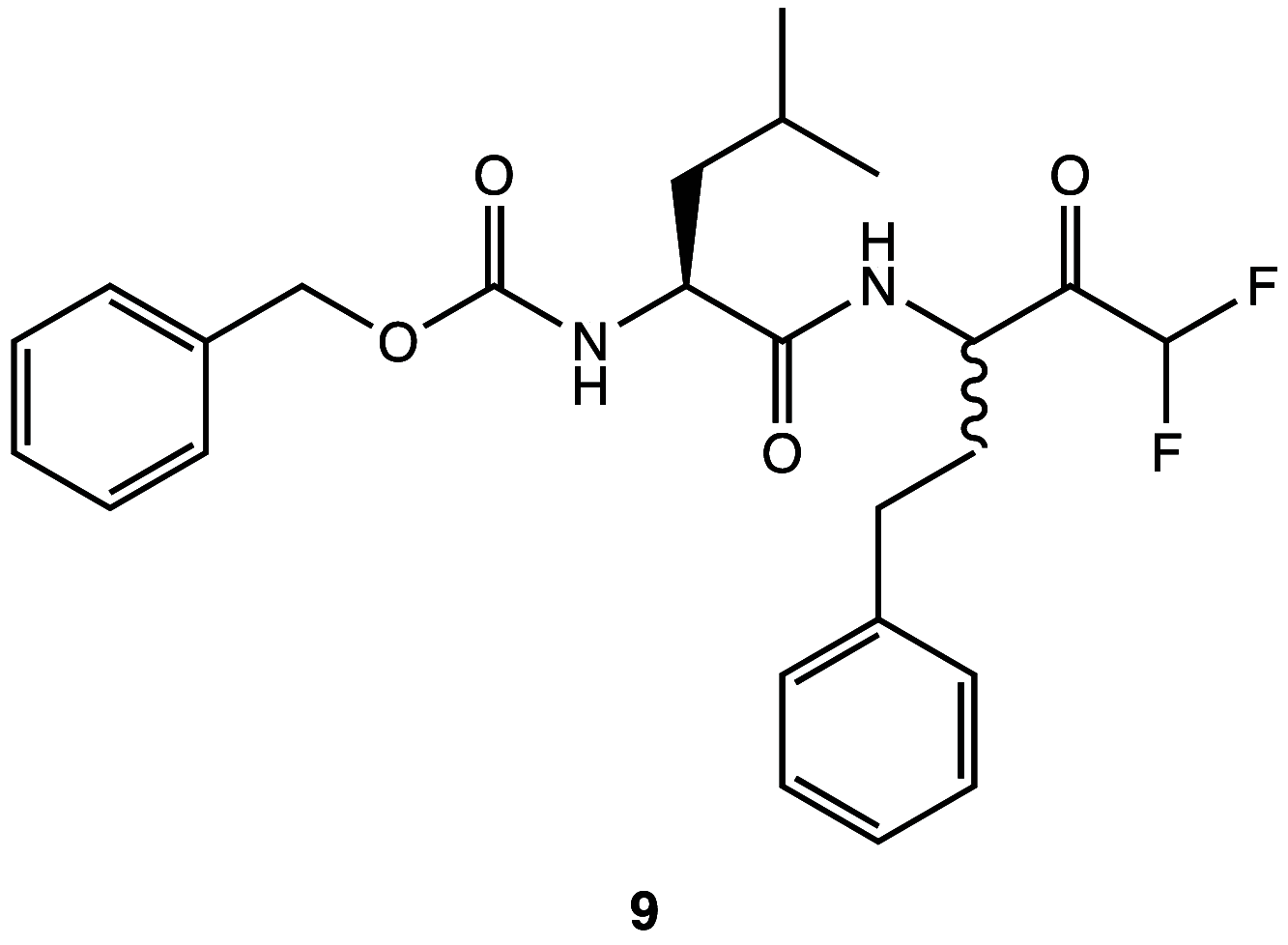
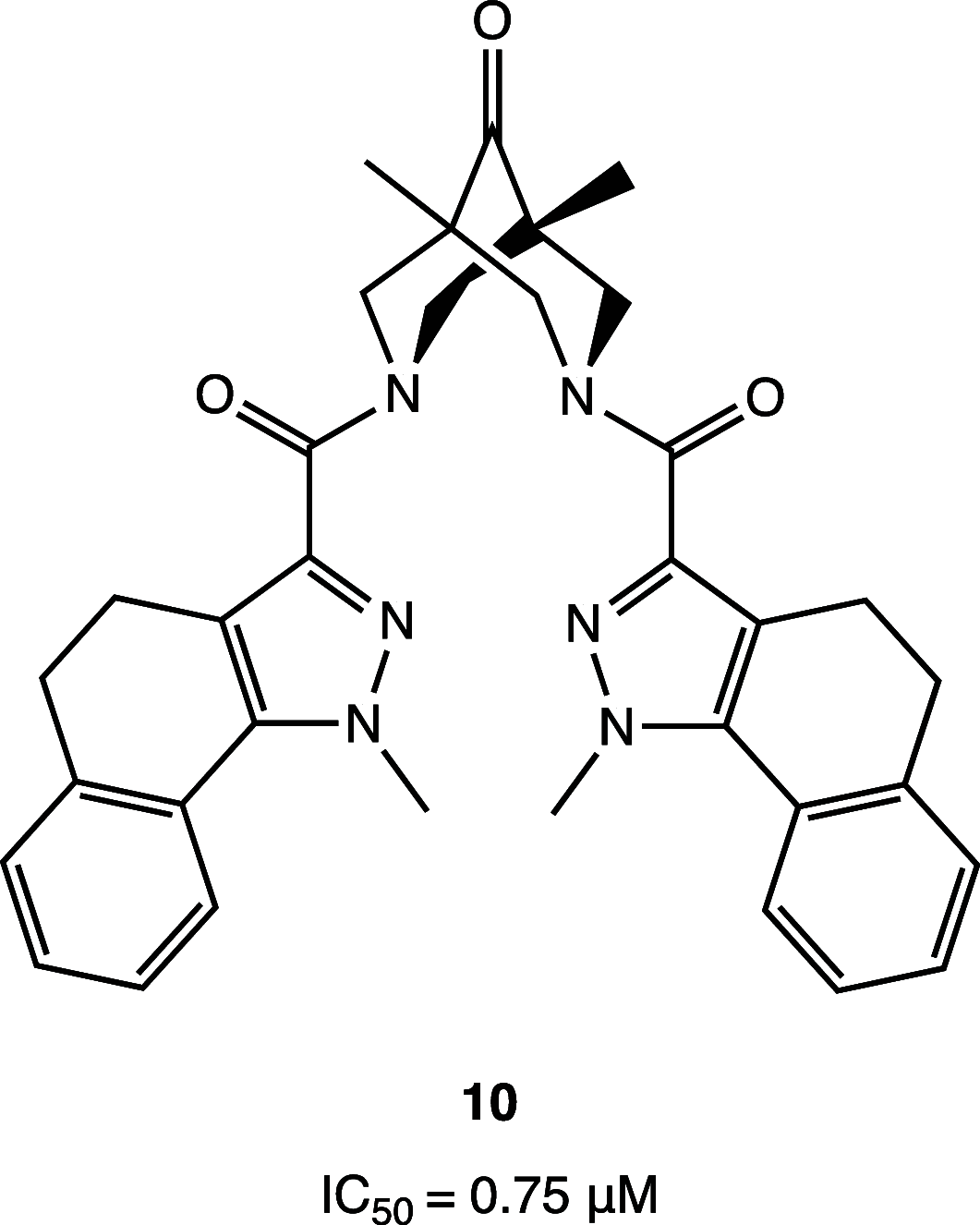
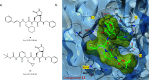
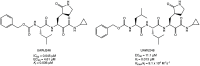
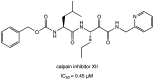
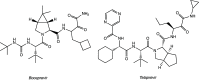
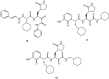
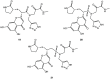
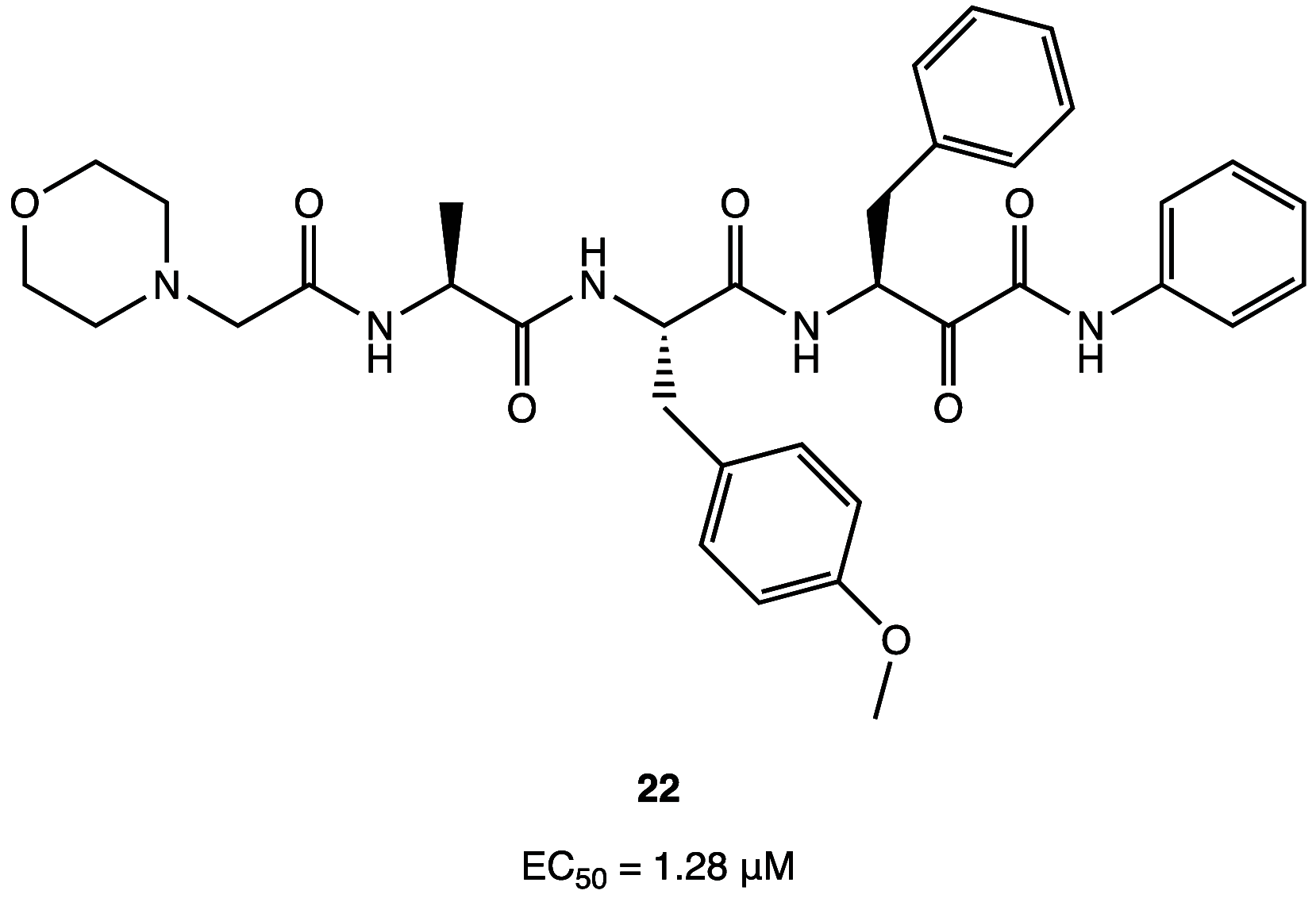
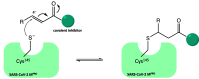
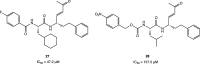
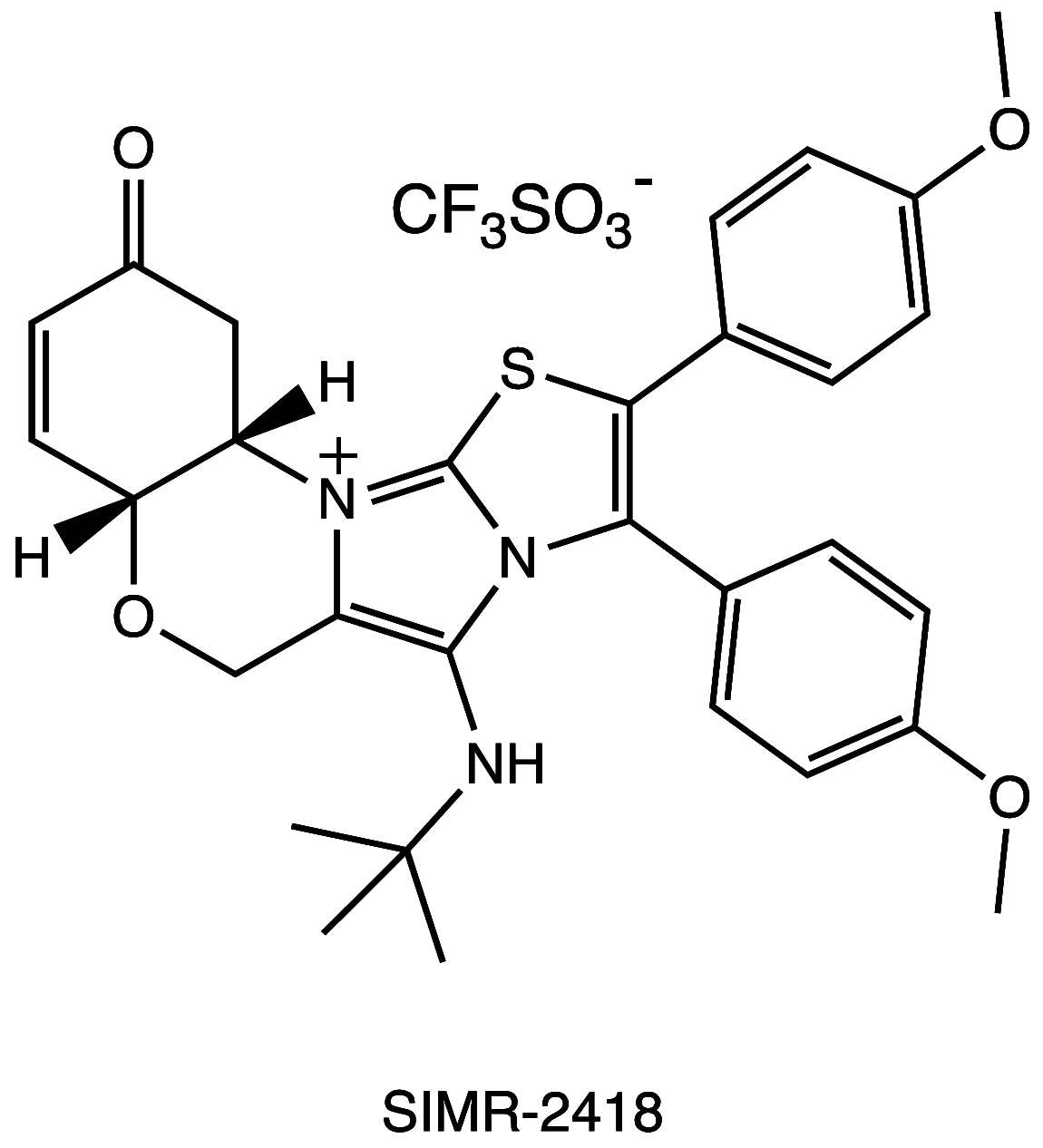
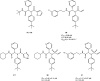
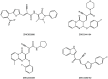
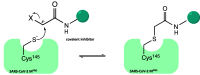

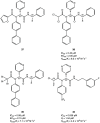
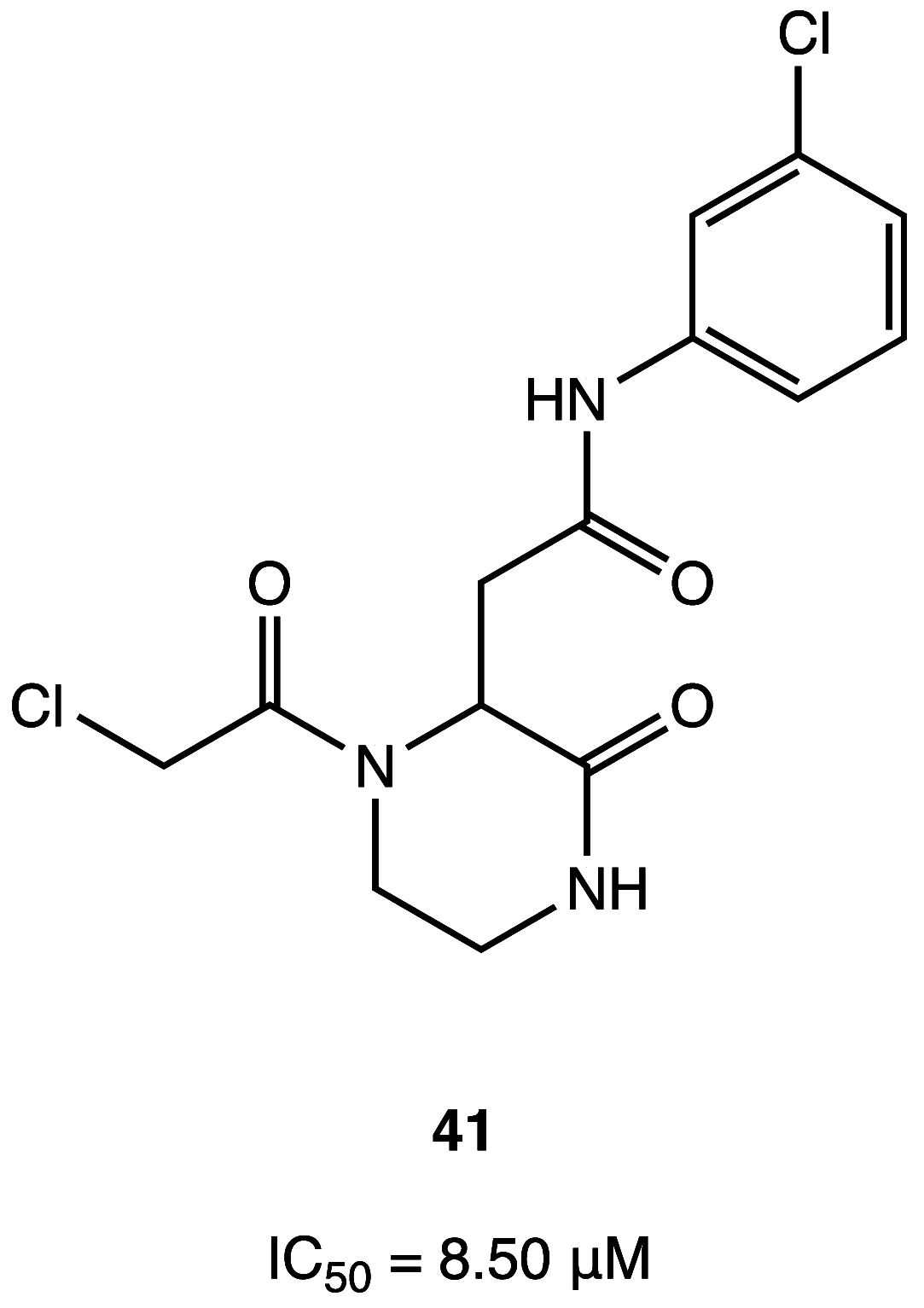
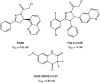
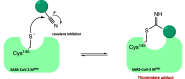
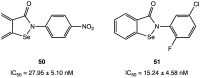
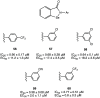
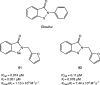
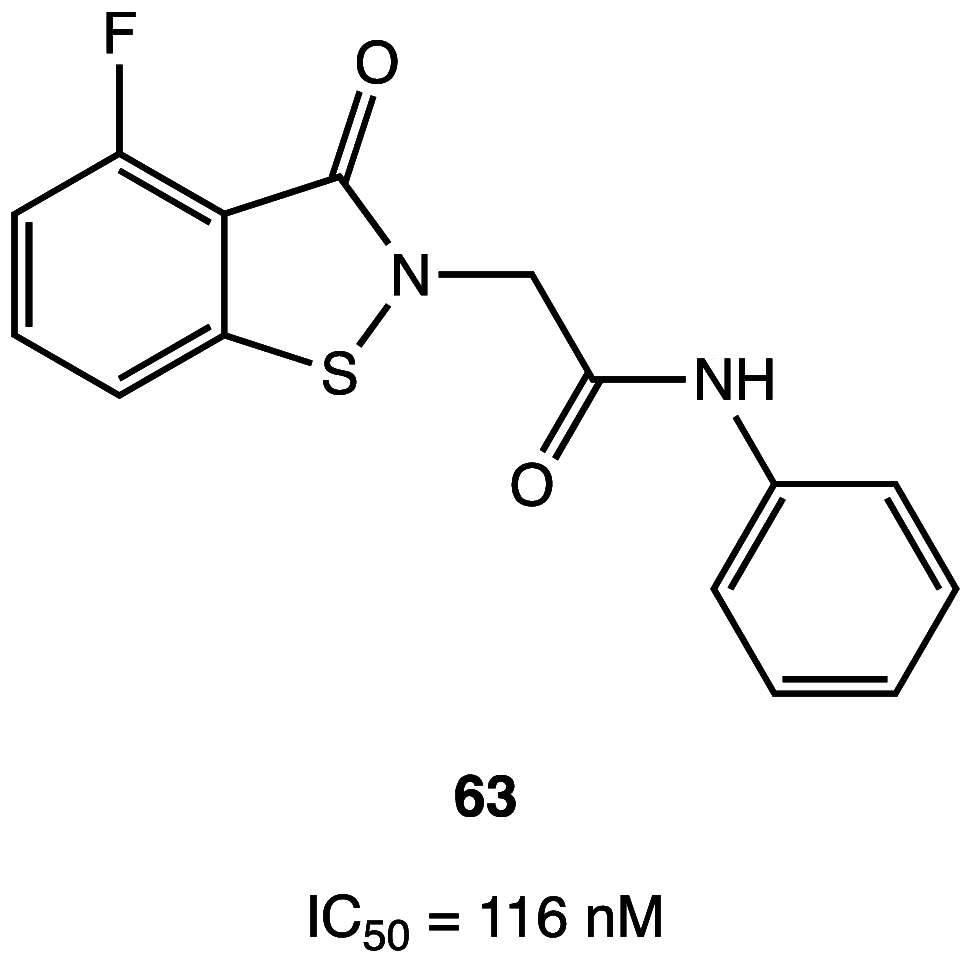
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

