Optimal MoCA cutoffs for detecting biologically-defined patients with MCI and early dementia
- PMID: 36169756
- PMCID: PMC9816212
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-022-06422-z
Optimal MoCA cutoffs for detecting biologically-defined patients with MCI and early dementia
Abstract
Objective: In this phase II psychometric study on the Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA), we tested the clinicometric properties of Italian norms for patients with mild cognitive impairment (PwMCI) and early dementia (PwD) and provided optimal cutoffs for diagnostic purposes.
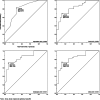
Methods: Retrospective data collection was performed for consecutive patients with clinically and biologically defined MCI and early dementia. Forty-five patients (24 PwMCI and 21 PwD) and 25 healthy controls were included. Raw MoCA scores were adjusted according to the conventional 1-point correction (Nasreddine) and Italian norms (Conti, Santangelo, Aiello). The diagnostic properties of the original cutoff (< 26) and normative cutoffs, namely, the upper limits (uLs) of equivalent scores (ES) 1, 2, and 3, were evaluated. ROC curve analysis was performed to obtain optimal cutoffs.
Results: The original cutoff demonstrated high sensitivity (0.93 [95% CI 0.84-0.98]) but low specificity (0.44 [0.32-0.56]) in discriminating between patients and controls. Nominal normative cutoffs (ES0 uLs) showed excellent specificity (SP range = 0.96-1.00 [0.88-1.00]) but poor sensitivity (SE range = 0.09-0.24 [0.04-0.36]). The optimal cutoff for Nasreddine's method was 23.50 (SE = 0.82 [0.71-0.90]; SP = 0.72 [0.60-0.82]). Optimal cutoffs were 20.97, 22.85, and 22.29 (SE range = 0.69-0.73 [0.57-0.83], SP range = 0.88-0.92 [0.77-0.97]) for Conti's, Santangelo's, and Aiello's methods, respectively.
Conclusion: Using the 1-point correction, combined with a cutoff of 23.50, might be useful in ambulatory settings with a large turnout. Our optimal cutoffs can offset the poor sensitivity of Italian cutoffs.
Keywords: Cutoff; Dementia; Mild Cognitive Impairment; Montreal Cognitive Assessment; Sensitivity; Specificity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical