ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022
- PMID: 36170152
- PMCID: PMC12642825
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001778
ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022
Abstract
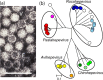
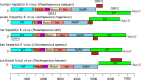
The family Hepeviridae includes enterically transmitted small quasi-enveloped or non-enveloped positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses infecting mammals and birds (subfamily Orthohepevirinae) or fish (Parahepevirinae). Hepatitis E virus (genus Paslahepevirus) is responsible for self-limiting acute hepatitis in humans; the infection may become chronic in immunocompromised individuals and extrahepatic manifestations have been described. Avian hepatitis E virus (genus Avihepevirus) causes hepatitis-splenomegaly syndrome in chickens. This is a summary of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Report on the family Hepeviridae, which is available at www.ictv.global/report/hepeviridae.
Keywords: Hepeviridae; ICTV report; hepatitis E virus; taxonomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

