Neurons burdened by DNA double-strand breaks incite microglia activation through antiviral-like signaling in neurodegeneration
- PMID: 36170369
- PMCID: PMC9519048
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo4662
Neurons burdened by DNA double-strand breaks incite microglia activation through antiviral-like signaling in neurodegeneration
Abstract
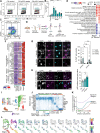
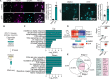
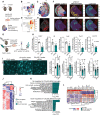
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are linked to neurodegeneration and senescence. However, it is not clear how DSB-bearing neurons influence neuroinflammation associated with neurodegeneration. Here, we characterize DSB-bearing neurons from the CK-p25 mouse model of neurodegeneration using single-nucleus, bulk, and spatial transcriptomic techniques. DSB-bearing neurons enter a late-stage DNA damage response marked by nuclear factor κB (NFκB)-activated senescent and antiviral immune pathways. In humans, Alzheimer's disease pathology is closely associated with immune activation in excitatory neurons. Spatial transcriptomics reveal that regions of CK-p25 brain tissue dense with DSB-bearing neurons harbor signatures of inflammatory microglia, which is ameliorated by NFκB knockdown in neurons. Inhibition of NFκB in DSB-bearing neurons also reduces microglia activation in organotypic mouse brain slice culture. In conclusion, DSBs activate immune pathways in neurons, which in turn adopt a senescence-associated secretory phenotype to elicit microglia activation. These findings highlight a previously unidentified role for neurons in the mechanism of disease-associated neuroinflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Lu T., Pan Y., Kao S.-Y., Li C., Kohane I., Chan J., Yankner B. A., Gene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain. Nature 429, 883–891 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen E., Beach T., Shen Y., Li R., Chang Y., Deficiency of the Mre11 DNA repair complex in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Mol. Brain Res. 128, 1–7 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG054012/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS113464/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 NS115064/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 NS115064/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062377/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM087237/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS102730/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG062335/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH119509/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058002/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008155/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS110453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG067151/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067151/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109978/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

