Effect of booster vaccination against Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants in Iceland
- PMID: 36171188
- PMCID: PMC9517986
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33076-4
Effect of booster vaccination against Delta and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants in Iceland
Abstract
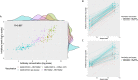
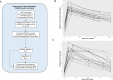
By the end of July 2021, the majority of the Icelandic population had received vaccination against COVID-19. In mid-July a wave of SARS-CoV-2 infections, dominated by the Delta variant, spread through the population, followed by an Omicron wave in December. A booster vaccination campaign was initiated to curb the spread of the virus. We estimate the risk of infection for different vaccine combinations using vaccination data from 276,028 persons and 963,557 qPCR tests for 277,687 persons. We measure anti-Spike-RBD antibody levels and ACE2-Spike binding inhibitory activity in 371 persons who received one of four recommended vaccination schedules with or without an mRNA vaccine booster. Overall, we find different antibody levels and inhibitory activity in recommended vaccination schedules, reflected in the observed risk of SARS-CoV-2 infections. We observe an increased protection following mRNA boosters, against both Omicron and Delta variant infections, although BNT162b2 boosters provide greater protection against Omicron than mRNA-1273 boosters.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of mRNA Vaccine Boosters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infection in Qatar.N Engl J Med. 2022 May 12;386(19):1804-1816. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2200797. Epub 2022 Mar 9. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 35263534 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of COVID-19 Incidence and Severity Among Adults Vaccinated With 2-Dose mRNA COVID-19 or Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines With and Without Boosters in Singapore.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Aug 1;5(8):e2228900. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.28900. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36018588 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination.Nat Med. 2022 Mar;28(3):481-485. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01705-6. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35051990 Free PMC article.
-
The Vaccine Efficacy Against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 13;10:940956. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940956. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35910897 Free PMC article.
-
Current German Recommendations and International Research on the Use of COVID-19 Boosters among Health Care Providers in 2024: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 25;60(3):385. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030385. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive analysis of the efficacy and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 26;13:945930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945930. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36090988 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and cellular immune durability of different COVID-19 vaccine platforms following homologous/heterologous boosters: one-year post vaccination.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 22;16:1526444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1526444. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39911379 Free PMC article.
-
The durability of natural infection and vaccine-induced immunity against future infection by SARS-CoV-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 2;119(31):e2204336119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204336119. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35858382 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing COVID-19 pandemic health responses in two high-income island nations: Iceland and New Zealand.Scand J Public Health. 2023 Jul;51(5):797-813. doi: 10.1177/14034948221149143. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Scand J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36717984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of mRNA Booster Vaccination Against Mild, Moderate, and Severe COVID-19 Caused by the Omicron Variant in a Large, Population-Based, Norwegian Cohort.J Infect Dis. 2022 Nov 28;226(11):1924-1933. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac419. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36259543 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

