Activation of the human insulin receptor by non-insulin-related peptides
- PMID: 36171189
- PMCID: PMC9519552
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33315-8
Activation of the human insulin receptor by non-insulin-related peptides
Abstract
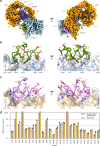
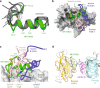
The human insulin receptor signalling system plays a critical role in glucose homeostasis. Insulin binding brings about extensive conformational change in the receptor extracellular region that in turn effects trans-activation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domains and downstream signalling. Of particular therapeutic interest is whether insulin receptor signalling can be replicated by molecules other than insulin. Here, we present single-particle cryoEM structures that show how a 33-mer polypeptide unrelated to insulin can cross-link two sites on the receptor surface and direct the receptor into a signalling-active conformation. The 33-mer polypeptide engages the receptor by two helical binding motifs that are each potentially mimicable by small molecules. The resultant conformation of the receptor is distinct from-but related to-those in extant three-dimensional structures of the insulin-complexed receptor. Our findings thus illuminate unexplored pathways for controlling the signalling of the insulin receptor as well as opportunities for development of insulin mimetics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.W., H.H., J.F.E., F.A.M., F.M.-O., Q.C., V.V.K., and D.G.B. are employees of Eli Lilly and Company. During employment, employees are minor stockholders in Eli Lilly and Company. A.L.A. is an employee of Advanced Testing Laboratory, a company that provides scientific services to Eli Lilly and Company. M.C.L, N.S.K., and M.B.M. received funding from Eli Lilly and Company to undertake the work described in the manuscript.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

