Stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent and oligometastatic soft tissue sarcoma
- PMID: 36171617
- PMCID: PMC9520802
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02781-1
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent and oligometastatic soft tissue sarcoma
Abstract
Background: Soft tissue sarcoma (STS) is a malignant tumor of highly heterogeneous mesenchymal origin. STS has a biological pattern and clinical transformation with localized invasive growth and is susceptible to hematogenous metastasis. Local therapeutic strategies may treat recurrent and oligometastatic STS, including surgery and radiation therapy. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for recurrent and oligometastatic STS.
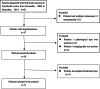
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 37 recurrent and oligometastatic STS patients with 58 lesions treated with SBRT from 2009 to 2019 at our institution. Oligometastatic is defined as metastatic lesions less than or equal to 3. The primary endpoint was local control (LC); secondary endpoints were survival and toxicity.
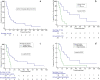
Results: The median follow-up was 21.0 months (3.0 to 125.0 months). Among 37 patients, 18 were recurrent patients, and 19 were oligometastatic patients. Median LC was 25.0 months (95% CI 20.0-45.0). The 1-, 2-, and 3-year LC rates were 80.2%, 58.3%, and 46.6%, respectively. Median overall survival (OS) was 24.0 months (95% CI 13.0-28.0), and the survival rates after SBRT were 71.5%, 40.0%, and 29.1% at 1, 2, and 3-year, respectively. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 10.0 months (95% CI 8.0-15.0 months), PFS rate after SBRT was 43.6%, 26.8%, and 18.4% at 1, 2, and 3 years, respectively. Late grade 3 radiation dermatitis was observed in one patient (2.7%). Using univariate and multivariate COX analysis, better OS, PFS, and LC were obtained in the histologic grade 1(G1) group, and tumor size and a number of lesions influenced LC.
Conclusions: SBRT is a safe and effective treatment for patients with recurrent and oligometastatic STS. Histological grade influences local control and survival. SBRT may be a promising treatment option for recurrent and oligometastatic STS.
Keywords: Oligometastatic; Radiotherapy; Recurrent; Soft tissue sarcoma (STS); Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic soft tissue sarcoma.Radiol Med. 2018 Nov;123(11):871-878. doi: 10.1007/s11547-018-0912-5. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Radiol Med. 2018. PMID: 29923086
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in recurrent, persistent or oligometastatic gynecological cancers.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Dec;159(3):611-617. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33059914
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Recurrent Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study From a Single Tertiary Center.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Jun;8(6):e70248. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70248. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40524140 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in the Management of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2020 May;40(5):2419-2428. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14211. Anticancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32366385 Review.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in metachronous oligometastatic prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis on the current prospective evidence.Br J Radiol. 2020 Dec 1;93(1116):20200496. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200496. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32822547 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of cystectomy in single-site oligometastatic bladder cancer: a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) study of 1,381 patients.Transl Androl Urol. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):81-90. doi: 10.21037/tau-24-586. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Transl Androl Urol. 2025. PMID: 39974803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Geel AN, Hoekstra HJ, van Coevorden F, Meyer S, Bruggink ED, Blankensteijn JD. Repeated resection of recurrent pulmonary metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1994;20(4):436–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

