Surgical and oncological outcomes of robotic- versus laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for advanced gastric cancer: a propensity score‑matched analysis of 1164 patients
- PMID: 36171631
- PMCID: PMC9520837
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-022-02778-w
Surgical and oncological outcomes of robotic- versus laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for advanced gastric cancer: a propensity score‑matched analysis of 1164 patients
Abstract
Background: Studies on surgical outcomes after robotic surgery are increasing; however, long-term oncological results of studies comparing robotic-assisted distal gastrectomy (RADG) versus laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy (LADG) for advanced gastric cancer (AGC) are still limited. This study aimed to assess the surgical and oncological outcomes of RADG and LADG for the treatment of AGC.
Methods: A total of 1164 consecutive AGC patients undergoing RADG or LADG were enrolled between January 2015 and October 2021. Propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis was performed to minimize selection bias. The perioperative and oncological outcomes between the two groups were compared.
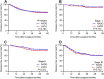
Results: Patient's characteristics were comparable between the two groups after PSM. RADG group represented a longer operative time (205.2 ± 43.1 vs 185.3 ± 42.8 min, P < 0.001), less operative blood loss (139.3 ± 97.8 vs 167.3 ± 134.2 ml, P < 0.001), greater retrieved lymph nodes (LNs) number (31.4 ± 12.1 vs 29.4 ± 12.3, P = 0.015), more retrieved LNs in the supra-pancreatic areas (13.4 ± 5.0 vs 11.4 ± 5.1, P < 0.001), and higher medical costs (13,608 ± 4326 vs 10,925 ± US $3925, P < 0.001) than LADG group. The overall complication rate was 13.7% in the RADG group and 16.6% in the LADG group, respectively; the difference was not significantly different (P = 0.242). In the subgroup analysis, the benefits of RADG were more evident in high BMI patients. Moreover, the 3-year overall survival (75.5% vs 73.1%, P = 0.471) and 3-year disease-free survival (72.9% vs 71.4%, P = 0.763) were similar between the two groups.
Conclusion: RADG appears to be a safe and feasible procedure and could serve as an alternative treatment for AGC in experienced centers.
Keywords: Advanced gastric cancer; Laparoscopic distal gastrectomy; Oncologic outcome; Robotic distal gastrectomy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Comparison of short-term efficacy between robotic and 3D laparoscopic-assisted D2 radical distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 25;23(4):350-356. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200224-00085. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32306602 Chinese.
-
Robotic- versus laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for advanced gastric cancer based on propensity score matching: short-term outcomes at a high-capacity center.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 16;10(1):6502. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63616-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32300209 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and long-term outcomes of totally robotic versus robotic-assisted radical distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: a mono-institution retrospective study.World J Surg Oncol. 2019 Nov 11;17(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1722-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31711530 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of laparoscopy-assisted by conventional open distal gastrectomy and extraperigastric lymph node dissection in early gastric cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2005 Jul 1;91(1):90-4. doi: 10.1002/jso.20271. J Surg Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15999352 Review.
-
Open, Laparoscopy-assisted, Robotic-assisted Distal Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: Evidence from Randomized Clinical Trials.Anticancer Res. 2024 Sep;44(9):3737-3745. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17198. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39197930 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Role of Robotic Surgery Gastric Cancer Treatment: A Comprehensive Review by the Robotic Global Surgical Society (TROGSS) and European Federation International Society for Digestive Surgery (EFISDS) Joint Working Group.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jan 31;32(2):83. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32020083. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39996883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive assessment of body mass index effects on short-term and long-term outcomes in laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 15;14(1):13842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64459-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38879651 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of robotic vs. laparoscopic gastrectomy for patients with gastric cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2024 Dec 1;110(12):8045-8056. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001826. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38874467 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: The Largest Systematic Reviews of 68,755 Patients and Meta-analysis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Jan;32(1):351-373. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16371-w. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39419891 Review.
-
Robotic vs laparoscopic distal gastrectomy with Billroth I and II reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Robot Surg. 2024 Dec 19;19(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-02193-1. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 39699804
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Beyer K, Baukloh AK, Kamphues C, Seeliger H, Heidecke CD, Kreis ME, Patrzyk M. Laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. World J Surg Oncol. 2019;17:68. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1600-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khaled I, Priego P, Soliman H, Faisal M, Saad Ahmed I. Oncological outcomes of laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19:206. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02322-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

