Methanol extraction revealed anticancer compounds Quinic Acid, 2(5H)‑Furanone and Phytol in Andrographis paniculata
- PMID: 36172002
- PMCID: PMC9511679
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2022.2584
Methanol extraction revealed anticancer compounds Quinic Acid, 2(5H)‑Furanone and Phytol in Andrographis paniculata
Abstract
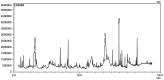
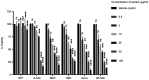
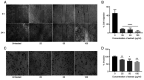
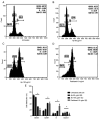
Andrographis paniculata (Ap) has been a part of traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory effects, treatment of snake bites and liver abnormalities. Several investigations have revealed its bioactive components to be andrographolides. The methanolic extracts of leaves from Ap were characterized, the non-andrographolides were identified and screened for anti-proliferative activity. The extracts showed significant toxicity against numerous cancer cells including HeLa, MCF7, BT549, 293 and A549 cells. Anti-proliferative activity and effect on cancer cell invasion (metastatic potential) and cell migration were examined. The extracts revealed significant inhibition of the ability of HeLa cells in repairing the gap created by a vertical wound made on a confluent cell monolayer. Similarly, a 40% reduction in cell migration was observed in presence of the extracts. Significant anti-angiogenic activity in terms of reduced blood capillary formation was observed on the Chorioallantoic membranes of embryonated hen eggs co-inoculated with HeLa cells and the extracts. Analysis of HeLa cells treated with the extracts using flow cytometry indicated the arrest of cell cycle progression at the G2/M phase. Variation in the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and elevated caspase-3 levels by immunoblotting confirmed cell death induction via the apoptotic pathway. Investigation of the extracts by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry displayed the predominant components to be 2(5H)-Furanone (14.73%), Quinic acid (17.32%), and Phytol (11.43%). These components have been previously known to have anticancer activity, while being studied individually in other plants. This is the first study, to the best of our knowledge, on the anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic activity of the non-andrographolide components from Ap.
Keywords: Andrographis paniculata; anti-angiogenic activity; anti-proliferative activity; apoptosis; cell cycle arrest.
Copyright: © Anoor et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ouhtit A, Gaur RL, Abdraboh M, Ireland SK, Rao PN, Raj SG, Al-Riyami H, Shanmuganathan S, Gupta I, Murthy SN, et al. Simultaneous inhibition of cell-cycle, proliferation, survival, metastatic pathways and induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells by a phytochemical super-cocktail: Genes that underpin its mode of action. J Cancer. 2013;4:703–715. doi: 10.7150/jca.7235. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sukanya SL, Sudisha J, Hariprasad P, Niranjana SR, Prakash HS, Fathima SK. Antimicrobial activity of leaf extracts of Indian medicinal plants against clinical and phytopathogenic bacteria. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8:6677–6682.
-
- Abutbul S, Golan-Goldhirsh A, Barazani O, Ofir R, Zilberg D. Screening of desert plants for use against bacterial pathogens in fish. Isr J Aquacult-Bamid. 2005;57:71–80.
-
- Pandey G, Madhuri S. Significance of fruits and vegetables in malnutrition cancer. Plant Arch. 2010;10:517–22.
-
- Pandey G, Madhuri S, Mandloi AK. Medicinal plants useful in fish diseases. Plant Arch. 2012;12:1–4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
