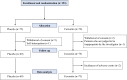
Effects of high-absorption curcumin for the prevention of hypertensive heart disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical study
- PMID: 36172003
- PMCID: PMC9512148
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeac057
Effects of high-absorption curcumin for the prevention of hypertensive heart disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical study
Abstract
Aims: Hypertension is a strong risk factor for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Curcumin has p300-specific histone acetyltransferase inhibitory activity, suppresses cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and fibrosis, and significantly reduces myocardial brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) expression without altering blood pressure in a rat model of hypertensive heart disease. This double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized study, for the first time, aimed to examine the efficacy of a high-absorption curcumin for the prevention of hypertensive heart disease in humans.
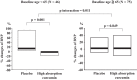
Methods and results: Patients exhibiting initial signs of hypertensive heart disease with left ventricular ejection fraction ≥60% and stable blood pressure <140/90 mmHg orally took a double-blinded capsule (either a 90 mg curcumin capsule or placebo) twice daily for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was per cent changes in left ventricular diastolic function (E/E') from baseline to 6 months after administration. The secondary endpoint was the per cent change in plasma BNP levels. The E/E' ratio per cent change from baseline to 6 months after administration was similar between the placebo (n = 69) and the curcumin (n = 73) groups. The per cent change in plasma BNP levels was significantly lower in the curcumin group than in the placebo group. In patients <65 years, BNP per cent changes were significantly lower in the curcumin group than in the placebo group, but similar between groups in ≥65 years (<65 vs. ≥65 years: P for interaction = 0.011).
Conclusions: A high-absorption curcumin agent did not affect the E/E' ratio, rather it significantly inhibited the increase in plasma BNP levels in patients with initial signs of hypertensive heart disease.
Keywords: B-type natriuretic peptide; Cardiac hypertrophy; Curcumin; Diastolic dysfunction; Hypertension; Prevention.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Crespo-Leiro MG, Farmakis D, Gilard M, Heymans S, Hoes AW, Jaarsma T, Jankowska EA, Lainscak M, Lam CSP, Lyon AR, McMurray JJV, Mebazaa A, Mindham R, Muneretto C, Francesco Piepoli M, Price S, Rosano GMC, Ruschitzka F, Kathrine Skibelund A; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021;42:3599–3726. - PubMed
-
- Maddox TM, Januzzi JL, Allen LA, Breathett K, Butler J, Davis LL, Fonarow GC, Ibrahim NE, Lindenfeld JA, Masoudi FA, Motiwala SR, Oliveros E, Patterson JH, Walsh MN, Wasserman A, Yancy CW, Youmans QR. 2021 update to the 2017 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for optimization of heart failure treatment: answers to 10 pivotal issues about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021;77:772–810. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto S, Kawamura T, Morimoto T, Ono K, Wada H, Kawase Y, Matsumori A, Nishio R, Kita T, Hasegawa K. Histone acetyltransferase activity of p300 is required for the promotion of left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in adult mice in vivo. Circulation 2006;113:679–690. - PubMed
-
- Menon VP, Sudheer AR. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol 2007;595:105–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous