Engineered Hybrid Treg-Targeted Nanosomes Restrain Lung Immunosuppression by Inducing Intratumoral CD8+T Cell Immunity
- PMID: 36172007
- PMCID: PMC9512414
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S346341
Engineered Hybrid Treg-Targeted Nanosomes Restrain Lung Immunosuppression by Inducing Intratumoral CD8+T Cell Immunity
Abstract
Introduction: Tumor immunotherapy is a key therapeutic paradigm for the treatment of several malignancies. However, in metastatic lung cancer, classical immunotherapy regimes are ineffective due to regulatory T cell (Treg)-related immunosuppression and tumor relapse.
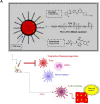
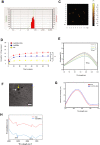
Materials: To address this issue, we designed specific biocompatible Treg-targeted nanocarriers (NCs) as a model of immune-based nanotherapy, in order to target Treg-related immunosuppression in the lung tumor microenvironment. This is achieved through the combination of Dasatinib and Epacadostat integrated into biodegradable nanosomes which can inhibit and reverse Treg-supporting immunosuppression. Flow cytometry and immunofluorescence analysis, PET/CT scan, PTT/PA imaging and the Balb/c tumor model were used to explore the anti-tumor effect of Treg-targeted NCs both in vitro and in vivo.
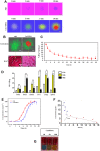
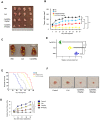
Results: Findings reveal that NC treatment triggered substantial tumor cell apoptosis and drastically decreased tumor volume followed by downregulation of Ki-67 antigen expression, respectively. Drug circulation time was also increased as shown by biodistribution analysis accompanied by greater accumulation in lung and peripheral tissues. Intratumoral Th1 cytokines' expression was also increased, especially TNF-A, IL-12 by 42%, and IL-6 by 18% compared to PBS treatment. In addition, the presence of mature CD80+/CD86+dendritic cells (DCs) revealed T cell enrichment and a decline in MDSC infiltration and myeloid subsets. Interestingly, a significant decline of Gr/CD11b myeloid cell population in blood and tissue samples was also observed. This immune activation can be attributed to the enhanced PTT efficiency and tumor targeting ability of the nanospheres which under near infrared (NIR) exposure can prompt highly efficient tumor ablation. We also demonstrated their therapeutic efficacy against 4T1 metastatic breast cancer model. Additionally, the photothermal therapy in combination with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade therapy exerted long-term tumor control over both primary and distant tumors.
Discussion: Overall, our findings present a novel nano-enabled platform for the inhibition of Treg-dependent immunosuppression in NSCLC and provide a novel nanotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of metastatic neoplasia.
Keywords: T cells; Tregs; immunosuppression; metastasis; nanosomes.
© 2022 Domvri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Dual photothermal MDSCs-targeted immunotherapy inhibits lung immunosuppressive metastasis by enhancing T-cell recruitment.Nanoscale. 2020 Apr 3;12(13):7051-7062. doi: 10.1039/d0nr00080a. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32186564
-
ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3392-3416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537094 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-induced peripheral immunosuppression promotes brain metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Sep;68(9):1501-1513. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02384-y. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31489465 Free PMC article.
-
Immune modulations during chemoimmunotherapy & novel vaccine strategies--in metastatic melanoma and non small-cell lung cancer.Dan Med J. 2013 Dec;60(12):B4774. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24355457 Review.
-
Treg-mediated acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors.Cancer Lett. 2019 Aug 10;457:168-179. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 9. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 31078738 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T cells in lung disease and transplantation.Biosci Rep. 2023 Oct 31;43(10):BSR20231331. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231331. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37795866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of Nano-drug Delivery Technology in Overcoming Drug Resistance in Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 20;27(11):864-872. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.101.30. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39800482 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Treg Cell Therapeutic Strategies for Breast Cancer: Holistic to Local Aspects.Cells. 2024 Sep 11;13(18):1526. doi: 10.3390/cells13181526. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling regulatory T lymphocytes within the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer via radiomics.Cancer Med. 2023 Dec;12(24):21861-21872. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6757. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 38083903 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in copper sulfide nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Aug 13;34:102197. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102197. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40893366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

