Okadaic acid influences xenobiotic metabolism in HepaRG cells
- PMID: 36172076
- PMCID: PMC9489895
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2022-5033
Okadaic acid influences xenobiotic metabolism in HepaRG cells
Abstract
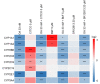
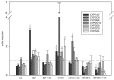
Okadaic acid (OA) is an algae-produced lipophilic marine biotoxin that accumulates in the fatty tissue of filter-feeding shellfish. Ingestion of contaminated shellfish leads to the diarrheic shellfish poisoning syndrome. Furthermore, several other effects of OA like genotoxicity, liver toxicity and tumor-promoting properties have been observed, probably linked to the phosphatase-inhibiting properties of the toxin. It has been shown that at high doses OA can disrupt the physical barrier of the intestinal epithelium. As the intestine and the liver do not only constitute a physical, but also a metabolic barrier against xenobiotic exposure, we here investigated the impact of OA on the expression of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and transporter proteins in human HepaRG cells liver cells in vitro at non-cytotoxic concentrations. The interplay of OA with known CYP inducers was also studied. Data show that the expression of various xenobiotic-metabolizing CYPs was downregulated after exposure to OA. Moreover, OA was able to counteract the activation of CYPs by their inducers. A number of transporters were also mainly downregulated. Overall, we demonstrate that OA has a significant effect on xenobiotic metabolism barrier in liver cells, highlighting the possibility for interactions of OA exposure with the metabolism of drugs and xenobiotics.
Keywords: CYP enzymes; HepaRG cells; okadaic acid.
Copyright © 2022 Wuerger et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Okadaic Acid Activates JAK/STAT Signaling to Affect Xenobiotic Metabolism in HepaRG Cells.Cells. 2023 Feb 28;12(5):770. doi: 10.3390/cells12050770. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899906 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of marine biotoxins on drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes and their regulation in mammalian cells.Arch Toxicol. 2024 May;98(5):1311-1322. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03694-6. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38416141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of hepatic effects of okadaic acid in HepaRG human liver cells.EXCLI J. 2023 Oct 31;22:1135-1145. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-6458. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 38054204 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of long-term versus short-term effects of okadaic acid on the apoptotic status of human HepaRG cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Feb 1;317:108937. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.108937. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 31926150
-
Okadaic acid (OA): Toxicity, detection and detoxification.Toxicon. 2019 Mar 15;160:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.12.007. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Toxicon. 2019. PMID: 30639658 Review.
Cited by
-
Okadaic Acid Activates JAK/STAT Signaling to Affect Xenobiotic Metabolism in HepaRG Cells.Cells. 2023 Feb 28;12(5):770. doi: 10.3390/cells12050770. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899906 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of marine biotoxins on drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes and their regulation in mammalian cells.Arch Toxicol. 2024 May;98(5):1311-1322. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03694-6. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38416141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of hepatic effects of okadaic acid in HepaRG human liver cells.EXCLI J. 2023 Oct 31;22:1135-1145. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-6458. eCollection 2023. EXCLI J. 2023. PMID: 38054204 Free PMC article.
-
Xeno-Free 3D Bioprinted Liver Model for Hepatotoxicity Assessment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 2;25(3):1811. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031811. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339088 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient environment improves drug metabolic activity in human iPSC-derived hepatocytes and HepG2.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04139-4. Online ahead of print. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40794106
References
-
- Belghit I, Varunjikar M, Lecrenier M-C, Steinhilber AE, Niedzwiecka A, Wang YV, et al. Future feed control – Tracing banned bovine material in insect meal. Food Control. 2021;128:108183. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108183. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
