Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 36172197
- PMCID: PMC9512262
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.999404
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
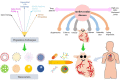
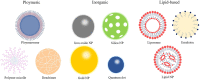
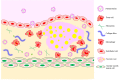
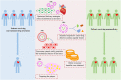
Cardiovascular disease is the most common health problem worldwide and remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Despite recent advances in the management of cardiovascular diseases, pharmaceutical treatment remains suboptimal because of poor pharmacokinetics and high toxicity. However, since being harnessed in the cancer field for the delivery of safer and more effective chemotherapeutics, nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems have offered multiple significant therapeutic effects in treating cardiovascular diseases. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems alter the biodistribution of therapeutic agents through site-specific, target-oriented delivery and controlled drug release of precise medicines. Metal-, lipid-, and polymer-based nanoparticles represent ideal materials for use in cardiovascular therapeutics. New developments in the therapeutic potential of drug delivery using nanoparticles and the application of nanomedicine to cardiovascular diseases are described in this review. Furthermore, this review discusses our current understanding of the potential role of nanoparticles in metabolism and toxicity after therapeutic action, with a view to providing a safer and more effective strategy for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; drug delivery; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; nanotoxicity.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Xue, Wang and Diao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akagi S., Nakamura K., Matsubara H., Kondo M., Miura D., Matoba T., et al. (2016). Intratracheal administration of prostacyclin analogue-incorporated nanoparticles ameliorates the development of monocrotaline and sugen-hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 67 (4), 290–298. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000352 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baigent C., Baigent L., Blackwell R., Collins J., Emberson J., Godwin R., et al. (2009). Aspirin in the primary and secondary prevention of vascular disease: Collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet 373 (9678), 1849–1860. 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60503-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

