Quantitative trait loci mapping reveals important genomic regions controlling root architecture and shoot biomass under nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium stress in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
- PMID: 36172562
- PMCID: PMC9511887
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.994666
Quantitative trait loci mapping reveals important genomic regions controlling root architecture and shoot biomass under nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium stress in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
Abstract
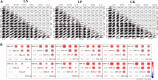
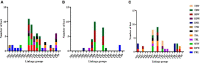
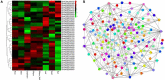
Plants rely on root systems for nutrient uptake from soils. Marker-assisted selection helps breeders to select desirable root traits for effective nutrient uptake. Here, 12 root and biomass traits were investigated at the seedling stage under low nitrogen (LN), low phosphorus (LP), and low potassium (LK) conditions, respectively, in a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, which was generated from Brassica napus L. Zhongshuang11 and 4D122 with significant differences in root traits and nutrient efficiency. Significant differences for all the investigated traits were observed among RILs, with high heritabilities (0.43-0.74) and high correlations between the different treatments. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping identified 57, 27, and 36 loci, explaining 4.1-10.9, 4.6-10.8, and 4.9-17.4% phenotypic variances under LN, LP, and LK, respectively. Through QTL-meta analysis, these loci were integrated into 18 significant QTL clusters. Four major QTL clusters involved 25 QTLs that could be repeatedly detected and explained more than 10% phenotypic variances, including two NPK-common and two specific QTL clusters (K and NK-specific), indicating their critical role in cooperative nutrients uptake of N, P, and K. Moreover, 264 genes within the four major QTL clusters having high expressions in roots and SNP/InDel variations between two parents were identified as potential candidate genes. Thirty-eight of them have been reported to be associated with root growth and development and/or nutrient stress tolerance. These key loci and candidate genes lay the foundation for deeper dissection of the NPK starvation response mechanisms in B. napus.
Keywords: Brassica napus L.; QTL mapping; candidate genes; major QTL; nutrient uptake.
Copyright © 2022 Ahmad, Ibrahim, Tian, Kuang, Wang, Wang and Dun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes Controlling Root Development Using a Recombinant Inbred Line Population in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 26;23(9):4781. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094781. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563170 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of root morphological traits as related to potassium use efficiency in rapeseed under two contrasting potassium levels by hydroponics.Sci China Life Sci. 2019 Jun;62(6):746-757. doi: 10.1007/s11427-018-9503-x. Epub 2019 May 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31069628 Review.
-
Integrating genome-wide association study with transcriptomic data to predict candidate genes influencing Brassica napus root and biomass-related traits under low phosphorus conditions.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023 Oct 4;16(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13068-023-02403-2. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2023. PMID: 37789456 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait loci for root morphology in response to low phosphorus stress in Brassica napus.Theor Appl Genet. 2010 Jun;121(1):181-93. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1301-1. Epub 2010 Mar 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2010. PMID: 20217384
-
Nutrient deficiency effects on root architecture and root-to-shoot ratio in arable crops.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 4;13:1067498. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1067498. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36684760 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blueprints for sustainable plant production through the utilization of crop wild relatives and their microbiomes.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 10;16(1):6364. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61779-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40640143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating genome assembly, structural variation map construction and GWAS reveal the impact of SVs on agronomic traits of Brassica napus.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Jul 26;138(8):191. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-04977-x. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 40715521
-
Insights on Phytohormonal Crosstalk in Plant Response to Nitrogen Stress: A Focus on Plant Root Growth and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 11;24(4):3631. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043631. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alcock T. D., Havlickova L., He Z., Wilson L., Bancroft I., White P. J., et al. (2018). Species-wide variation in shoot nitrate concentration, and genetic loci controlling nitrate, phosphorus and potassium accumulation in Brassica napus L. Front. Plant Sci. 871:1487. 10.3389/fpls.2018.01487 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amoah N. K. A., Akromah R., Kena A. W., Manneh B., Dieng I., Bimpong I. K. (2020). Mapping QTLs for tolerance to salt stress at the early seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using a newly identified donor ‘Madina Koyo’. Euphytica 216:156. 10.1007/s10681-020-02689-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

