T cell receptor variable β 20-1 harbors a nucleotide binding pocket in the CDR2 β loop
- PMID: 36172593
- PMCID: PMC7613644
- DOI: 10.4236/oji.2013.33021
T cell receptor variable β 20-1 harbors a nucleotide binding pocket in the CDR2 β loop
Abstract
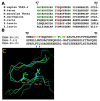
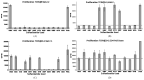
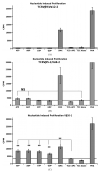
Novel aspects of T cells containing TCRVβ20-1 are numerous, ranging from pathogen specific reactivity to specific tissue homing, or possible T cell subsets. Recently, it was demonstrated that TCR itself could become reactive by binding to small molecules free of the pHLA interface. Our work here was to identify a natural ligand binding to an identified pocket on the CDR2β loop of these TCR. Using docking of suspected ligands, we were able to show Guanine and Adenine di- and tri-nucleotides readily bind to the identified site. Comparing these with small molecule sites found on other TCR types, we show this interaction is novel. With further molecular dynamic simulations, these sites are shown to be plausible by conducting simple computational based solubility tests as cross validation. Combined with simple proliferative responses, the identified nucleotides are also shown to have functional consequences by inducing T cell proliferation for CD4/Vβ20-1 + T cells, while failing to induce proliferation in other T cell isolates. Merging computational and simple cell assays, this work establishes a role of nucleotides in T cells found to contain this TCR sub-type.
Keywords: Adverse Drug Reactions; Autoimmune Diseases; T Cell Receptor; T Cell Receptor Variable Domain.
Figures


References
-
- Ko TM, Chung WH, Wei CY, Shih HY, Chen JK, et al. Shared and restricted T-cell receptor use is crucial for carbamazepine-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2011;128:1266–1276. - PubMed
-
- Komatsu T, Moriya N, Shiohara T. T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire and function of human epidermal T cells: Restricted TCR V alpha-V beta genes are utilized by T cells residing in the lesional epidermis in fixed drug eruption. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 1996;104:343–350. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.30738.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
