Effects of Moringa oleifera aqueous seed extracts on reproductive traits of heat-stressed New Zealand white female rabbits
- PMID: 36172616
- PMCID: PMC9510754
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.883976
Effects of Moringa oleifera aqueous seed extracts on reproductive traits of heat-stressed New Zealand white female rabbits
Abstract
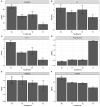
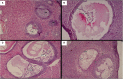
Heat stress is reported to have deleterious effects on rabbit physiology by impairing reproductive performances arising from free radical production due to oxidative stress. Plant extracts have been listed among efficient and healthy strategies for alleviating the effects of free radicals in the body of an animal. Numerous studies have documented the medicinal value of Moringa oleifera on various body functional systems although most of these data have not been scientifically validated. The growing concern of heat stress owing to the effects of global warming has affected animal productivity and even reproductive health, yet mitigation measures are still scanty. To this end, we investigated the efficacy of Moringa oleifera aqueous seed extract on selected in the alleviation of morphofunctional impairments on functional systems of the body. Here, we quantified the effects of Moringa oleifera seed extracts on reproductive performances, hormonal profile, and ovarian histology in the management of heat stress in female rabbits. We were particularly interested in testing the hypothesis that Moringa oleifera seed extracts do not have medicinal value in the mitigation of oxidative stress accompanying heat-stressed animals and, therefore, affecting growth performance and reproductive value. Twenty-eight female rabbits aged 6 months and weighing between 2015.6 and 2322.7 g were randomly assigned to four treatment groups of temperature, relative humidity, temperature humidity index, and M. oleifera seed extracts as follows: T0: ambient temperature (18-24°C), 59 ± 0.48%, 23.6 ± 1.52; T1, T2, and T3: 35-36°C, 64 ± 0.6%, 32.5 ± 0.7, followed by 100, 200, and 0 mg/kg b.w of M. oleifera seed extracts. Artificial heat was introduced in each rabbit cage from 08:00 h to 16:00 h. Reproductive performances related to female rabbits and relevant biodata of their young ones were recorded. All animals were sacrificed at the end of 80 days of experiments, and blood was collected for hormonal assays and ovary tissues for histology. Data on hormones and reproductive parameters of adult females as well as parameters related to kid performance and milk yield were subjected to one-way ANOVA, and significant differences among treatment subjects were analyzed using Tukey's post-hoc test at 5% significance level. The results revealed a significant decrease (P < 0.05) in food consumption, body weight, and body weight gain in pregnant and lactating female rabbits exposed to heat stress. A decrease in fur removal by mothers, litter size from birth to weaning, litter weight, kid body weight, and body weight gain in adult rabbits submitted to heat stress was observed. The findings were also reflected on weekly milk yield and daily milk efficiency as well as serum hormone levels. Following administration of M. oleifera seed extracts at 200 mg/kg b.w., there was significant increase (P < 0.05) in these parameters. On the contrary, an increase (P < 0.05) in the number of services per conception, milk intake, and serum progesterone level was initially observed in the same subjects, but upon administration of M. oleifera seed extracts, there was a significant decrease (P < 0.05) on these measures. Ovarian histology of animals at T0 and T2 treatments showed structural features comparable to those of controls. Overall, our results show that administration of M. oleifera seed extracts at 200 mg/kg b.w possesses therapeutic value to the effects of oxidative stress associated with heat stress. Further pharmacological evaluation on seed extracts of M. oleifera may yield the much-needed medicine in the treatment and management of poor animal productivity and reproductive health arising from severe weather associated with global warming.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; female rabbits; heat stress; oxidative stress; reproduction.
Copyright © 2022 Mutwedu, Nyongesa, Kitaa, Ayagirwe, Baharanyi and Mbaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effects of avocado (Persea americana Mill.) seed powder against reproductive toxicity induced by Mancozeb (herbicide) in female rabbits.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 8;9(7):e18057. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18057. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37483832 Free PMC article.
-
Ovario- protective effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative ovarian damage and reproductive dysfunction in female rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1054. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82921-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774723 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of Moringa oleifera leaf powder orally improved productive performance by enhancing the intestinal health in rabbits under chronic heat stress.J Therm Biol. 2020 Oct;93:102680. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2020.102680. Epub 2020 Aug 10. J Therm Biol. 2020. PMID: 33077107
-
A Review on the Antidiabetic Properties of Moringa oleifera Extracts: Focusing on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation as Main Therapeutic Targets.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 11;13:940572. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940572. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35899107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cultivation and Uses of Moringa oleifera as Non-Conventional Feed Stuff in Livestock Production: A Review.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;13(1):63. doi: 10.3390/life13010063. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36676012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
n-Butanol fraction of moringa seed attenuates arsenic intoxication by regulating the uterine inflammatory and apoptotic pathways.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(12):18593-18613. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32213-4. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38349492
-
Therapeutic effects of avocado (Persea americana Mill.) seed powder against reproductive toxicity induced by Mancozeb (herbicide) in female rabbits.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 8;9(7):e18057. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18057. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37483832 Free PMC article.
-
Ramifications of Heat Stress on Rabbit Production and Role of Nutraceuticals in Alleviating Its Negative Impacts: An Updated Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jul 11;12(7):1407. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071407. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Heat Stress on the Ovary, Follicles and Oocytes: A Systematic Review.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 5:2024.12.04.626831. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.04.626831. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biol Reprod. 2025 Jul 08:ioaf150. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioaf150. PMID: 39677695 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Nardone A, Ronchi B, Lacetera N, Ranieri MS, Bernabucci U. Effects of climate changes on animal production and sustainability of livestock systems. Liv Sci. (2010) 130:57–69. 10.1016/j.livsci.2010.02.011 - DOI
-
- Kumar SBV, Kumar A, Kataria M. Effects of heat stress in tropical livestock and different strategies for its amelioration. J stress Physiol and Biochem. (2011) 7:45–54.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

