Antibiotics Resistance Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Strains in Northwest China
- PMID: 36172620
- PMCID: PMC9512286
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S383444
Antibiotics Resistance Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Strains in Northwest China
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to estimate the resistance rate of Helicobacter pylori (HP) to commonly used antibiotics and analyze the potential influencing factors in northwest regions of China.
Patients and methods: HP-positive patients visiting the outpatient department of multiple hospitals were enrolled in the study. Then, gastric mucosal biopsy specimens were collected for HP isolation, culture, and investigation of the resistance rate of HP to amoxicillin, metronidazole, tetracycline, levofloxacin, and clarithromycin by Epsilometer test (E-test) antibiotic susceptibility testing. In addition, multi-drug resistance, the influence of HP eradication history, age, and region of residence on drug resistance rate were analyzed.
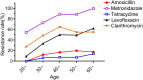
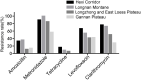
Results: In total, 198 HP clinical strains were successfully isolated and cultured. The resistance rates of amoxicillin, metronidazole, tetracycline, levofloxacin, and clarithromycin were 16.16%, 85.86%, 7.58%, 46.46%, and 55.05%, respectively. The multi-drug resistance rates demonstrated that dual and triple resistances were 30.30% and 22.73%, respectively. The quadruple resistance rate reached 9.60%. Our results revealed that the prior eradication history of HP significantly increased levofloxacin and clarithromycin resistance. Metronidazole and levofloxacin resistances significantly differed among different age groups, which presented an upward trend with increasing age. Drug resistance rates varied with geographic regions, especially amoxicillin and clarithromycin resistance, which were highest in Hexi Corridor and Longnan regions.
Conclusion: The current situation of HP resistance to common antibiotics is severe. Tetracycline is the most sensitive antibiotic, followed by amoxicillin, the first choice for HP eradication. However, the eradication failure of HP may lead to an increase in the resistance rate. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the standardized diagnosis and treatment of HP to improve the primary eradication rate.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; antibiotic; drug resistance; eradication.
© 2022 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of previous eradication failure on antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori: A retrospective study over 8 years in Beijing.Helicobacter. 2021 Aug;26(4):e12804. doi: 10.1111/hel.12804. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Helicobacter. 2021. PMID: 33860967
-
Antibiotic resistance status of helicobacter pylori strains isolated from initial eradication patients in Ningbo, China, from 2017 to 2021.Helicobacter. 2022 Oct;27(5):e12920. doi: 10.1111/hel.12920. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Helicobacter. 2022. PMID: 35939548
-
[Preliminary study on in-vitro induction of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Sep;45(9):708-11. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18021568 Chinese.
-
Primary Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori in China.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 May;62(5):1146-1154. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4536-8. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28315035 Review.
-
Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 5;7:168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00168. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28529929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clarithromycin sustained-release tablet may be an improper therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep 14;17:17562848241275332. doi: 10.1177/17562848241275332. eCollection 2024. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39290332 Free PMC article.
-
Can the optimal treatment duration be determined in bismuth-containing therapies for Helicobacter pylori eradication?Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):4037-4039. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01099-w. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37310656 No abstract available.
-
Success of susceptibility-guided eradication of Helicobacter pylori in a region with high secondary clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance rates.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 14;30(2):184-195. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i2.184. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38312120 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a genetic and physiological perspective.Gut Pathog. 2025 May 23;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00704-5. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40410811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Antibiotic Resistance in Patients Enrolled in Guangzhou, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Aug 3;16:5033-5038. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S418482. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37554543 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous