Cell-Specific Actions of the Prostaglandin E-Prostanoid Receptor 4 Attenuating Hypertension: A Dominant Role for Kidney Epithelial Cells Compared With Macrophages
- PMID: 36172956
- PMCID: PMC9673718
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026581
Cell-Specific Actions of the Prostaglandin E-Prostanoid Receptor 4 Attenuating Hypertension: A Dominant Role for Kidney Epithelial Cells Compared With Macrophages
Abstract
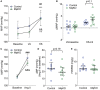
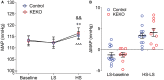
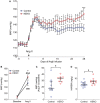
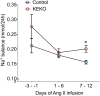
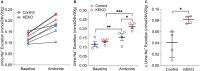
Background A beneficial role for prostanoids in hypertension is suggested by clinical studies showing nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which block the production of all prostanoids, cause sodium retention and exacerbate hypertension. Among prostanoids, prostaglandin E2 and its E-prostanoid receptor 4 receptor (EP4R) have been implicated in blood pressure control. Our previous study found that conditional deletion of EP4R from all tissues in adult mice exacerbates angiotensin II-dependent hypertension, suggesting a powerful effect of EP4R to resist blood pressure elevation. We also found that elimination of EP4R from vascular smooth muscle cells did not affect the severity of hypertension, suggesting nonvascular targets of prostaglandin E mediate this antihypertensive effect. Methods and Results Here we generated mice with cell-specific deletion of EP4R from macrophage-specific EP4 receptor knockouts or kidney epithelial cells (KEKO) to assess the contributions of EP4R in these cells to hypertension pathogenesis. Macrophage-specific EP4 receptor knockouts showed similar blood pressure responses to alterations in dietary sodium or chronic angiotensin II infusion as Controls. By contrast, angiotensin II-dependent hypertension was significantly augmented in KEKOs (mean arterial pressure: 146±3 mm Hg) compared with Controls (137±4 mm Hg; P=0.02), which was accompanied by impaired natriuresis in KEKOs. Because EP4R expression in the kidney is enriched in the collecting duct, we compared responses to amiloride in angiotensin II-infused KEKOs and Controls. Blockade of the epithelial sodium channel with amiloride caused exaggerated natriuresis in KEKOs compared with Controls (0.21±0.01 versus 0.15±0.02 mmol/24 hour per 20 g; P=0.015). Conclusions Our data suggest EP4R in kidney epithelia attenuates hypertension. This antihypertension effect of EP4R may be mediated by reducing the activity of the epithelial sodium channel, thereby promoting natriuresis.
Keywords: EP4 receptor; hypertension; kidney epithelial cells; prostaglandin E2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prostaglandin EP4 receptor is a master regulator of the expression of PGE2 receptors following inflammatory activation in human monocytic cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018 Oct;1863(10):1297-1304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018. PMID: 30053598
-
Vascular Smooth Muscle-Specific EP4 Receptor Deletion in Mice Exacerbates Angiotensin II-Induced Renal Injury.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Oct 20;25(12):642-656. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6592. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 27245461
-
VSMC-specific EP4 deletion exacerbates angiotensin II-induced aortic dissection by increasing vascular inflammation and blood pressure.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Apr 23;116(17):8457-8462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902119116. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30948641 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammation therapy by activation of prostaglandin EP4 receptor in cardiovascular and other inflammatory diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;59(2):116-23. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182244a12. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21697732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AT2 Receptors: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 2017 Apr 1;30(4):339-347. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpw121. Am J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 27664954 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of mitochondrial pyruvate transport initiates cardiac glycogen accumulation and heart failure.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 5:2024.06.06.597841. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.06.597841. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 38895296 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Prostanoids in Cardiac and Vascular Remodeling.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Mar;44(3):558-583. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320045. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38269585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The link between immunity and hypertension in the kidney and heart.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 9;10:1129384. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1129384. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36970367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

