Drug-food Interactions in the Era of Molecular Big Data, Machine Intelligence, and Personalized Health
- PMID: 36173075
- PMCID: PMC10258917
- DOI: 10.2174/2212798412666220620104809
Drug-food Interactions in the Era of Molecular Big Data, Machine Intelligence, and Personalized Health
Abstract
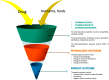
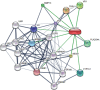
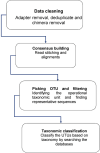
The drug-food interaction brings forth changes in the clinical effects of drugs. While favourable interactions bring positive clinical outcomes, unfavourable interactions may lead to toxicity. This article reviews the impact of food intake on drug-food interactions, the clinical effects of drugs, and the effect of drug-food in correlation with diet and precision medicine. Emerging areas in drug-food interactions are the food-genome interface (nutrigenomics) and nutrigenetics. Understanding the molecular basis of food ingredients, including genomic sequencing and pharmacological implications of food molecules, helps to reduce the impact of drug-food interactions. Various strategies are being leveraged to alleviate drug-food interactions; measures including patient engagement, digital health, approaches involving machine intelligence, and big data are a few of them. Furthermore, delineating the molecular communications across dietmicrobiome- drug-food-drug interactions in a pharmacomicrobiome framework may also play a vital role in personalized nutrition. Determining nutrient-gene interactions aids in making nutrition deeply personalized and helps mitigate unwanted drug-food interactions, chronic diseases, and adverse events from their onset. Translational bioinformatics approaches could play an essential role in the next generation of drug-food interaction research. In this landscape review, we discuss important tools, databases, and approaches along with key challenges and opportunities in drug-food interaction and its immediate impact on precision medicine.
Keywords: Drug-food interactions; big data; machine intelligence; nutrigenomics; pharmacomicrobiome.; precision medicine.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
KS received salary, consulting fees or honoraria from Philips Healthcare, Kencor Health, OccamzRazor, Alphabet, McKinsey& Company, BCG, LEK. KS has been an em- ployee of AstraZeneca at the time of publication. LS reports being a cofounder of Entrupy Inc, Velai Inc and Gaius Networks Inc, and has served as a consultant for the World Bank and the Governance Lab.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantum leap: is the conflux of artificial intelligence, personalized medicine, nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics the path to optimal health?Epigenomics. 2023 Apr;15(7):397-400. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0084. Epub 2023 May 16. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 37191059 No abstract available.
-
Precision Nutrition 4.0: A Big Data and Ethics Foresight Analysis--Convergence of Agrigenomics, Nutrigenomics, Nutriproteomics, and Nutrimetabolomics.OMICS. 2016 Feb;20(2):69-75. doi: 10.1089/omi.2015.0193. Epub 2016 Jan 19. OMICS. 2016. PMID: 26785082
-
Implementation of Nutrigenetics and Nutrigenomics Research and Training Activities for Developing Precision Nutrition Strategies in Malaysia.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 1;14(23):5108. doi: 10.3390/nu14235108. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in precision medicine: A paradigm shift in big data analysis.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022;190(1):57-100. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2022.03.002. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36008002
-
Polymorphisms, diet and nutrigenomics.J Prev Med Hyg. 2022 Oct 17;63(2 Suppl 3):E125-E141. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.2S3.2754. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Prev Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 36479483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of smart devices and the evolution of customized healthcare services focusing on big data: a systematic review.Mhealth. 2023 Dec 12;10:7. doi: 10.21037/mhealth-23-24. eCollection 2024. Mhealth. 2023. PMID: 38323151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Food interactions with tyrosine kinase inhibitors used to treat advanced renal cell carcinoma.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2025;29(1):1-10. doi: 10.5114/wo.2025.148229. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2025. PMID: 40330454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between nutrigenomics and low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets in personalized healthcare.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 23;12:1595316. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1595316. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40626223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of free-living diet composition with plasma lipoprotein(a) levels in healthy adults.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Sep 5;22(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01884-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37670291 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Food on the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of HA121-28 Tablet, a Novel Multi-Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Healthy Chinese Subjects: A Phase I Clinical Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 24;19:515-524. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S484310. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39876990 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Saito Y. Current status of health foods including their interactions with drugs and adverse events. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(12):1511–1516. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00155-1. [Available from https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/yakushi/ 138/12/138_18-00155-1/_art... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piscitelli S.C., Rodvold K.A. Drug interactions in infectious diseases 3rd Edition. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013;75(3):871. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3575955/
-
- Manasse H.R., Reilly C. Drug- Induced Diseases. American society of Health Pharmacists. 2010. Section 1 magnitude/significance of drug-induced diseases impact on the health care system drug safety and drug-induced disease: The regulatory , legal , and practice environments. In. James, E.T.; Douglas, A.M. (Eds.), .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

