Altered lung physiology in two cohorts after COVID-19 infection as assessed by computed cardiopulmonography
- PMID: 36173325
- PMCID: PMC9639770
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00436.2022
Altered lung physiology in two cohorts after COVID-19 infection as assessed by computed cardiopulmonography
Abstract
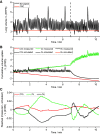
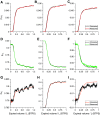
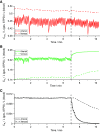
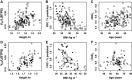
The longer-term effects of COVID-19 on lung physiology remain poorly understood. Here, a new technique, computed cardiopulmonography (CCP), was used to study two COVID-19 cohorts (MCOVID and C-MORE-LP) at both ∼6 and ∼12 mo after infection. CCP is comprised of two components. The first is collection of highly precise, highly time-resolved measurements of gas exchange with a purpose-built molecular flow sensor based around laser absorption spectroscopy. The second component is estimation of physiological parameters by fitting a cardiopulmonary model to the data set. The measurement protocol involved 7 min of breathing air followed by 5 min of breathing pure O2. One hundred seventy-eight participants were studied, with 97 returning for a repeat assessment. One hundred twenty-six arterial blood gas samples were drawn from MCOVID participants. For participants who had required intensive care and/or invasive mechanical ventilation, there was a significant increase in anatomical dead space of ∼30 mL and a significant increase in alveolar-to-arterial Po2 gradient of ∼0.9 kPa relative to control participants. Those who had been hospitalized had reductions in functional residual capacity of ∼15%. Irrespectively of COVID-19 severity, participants who had had COVID-19 demonstrated a modest increase in ventilation inhomogeneity, broadly equivalent to that associated with 15 yr of aging. This study illustrates the capability of CCP to study aspects of lung function not so easily addressed through standard clinical lung function tests. However, without measurements before infection, it is not possible to conclude whether the findings relate to the effects of COVID-19 or whether they constitute risk factors for more serious disease.NEW & NOTEWORTHY This study used a novel technique, computed cardiopulmonography, to study the lungs of patients who have had COVID-19. Depending on severity of infection, there were increases in anatomical dead space, reductions in absolute lung volumes, and increases in ventilation inhomogeneity broadly equivalent to those associated with 15 yr of aging. However, without measurements taken before infection, it is unclear whether the changes result from COVID-19 infection or are risk factors for more severe disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; human; laser absorption spectroscopy; lung volumes; respiratory dead space.
Conflict of interest statement
Oxford University Innovation, a wholly owned subsidiary of the University of Oxford, holds/has filed patents relating to the background IP for the technology. J.H.C., G.A.D.R., and P.A.R. have an interest in one or more patents. B.R. has consulted for Axcella therapeutics. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Mountain JE, Santer P, O’Neill DP, Smith NM, Ciaffoni L, Couper JH, Ritchie GA, Hancock G, Whiteley JP, Robbins PA. Potential for noninvasive assessment of lung inhomogeneity using highly precise, highly time-resolved measurements of gas exchange. J Appl Physiol (1985) 124: 615–631, 2018. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00745.2017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magor-Elliott SR, Fullerton CJ, Richmond G, Ritchie GA, Robbins PA. A dynamic model of the body gas stores for carbon dioxide, oxygen, and inert gases that incorporates circulatory transport delays to and from the lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 130: 1383–1397, 2021. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00764.2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cummings B, Hamilton ML, Ciaffoni L, Pragnell TR, Peverall R, Ritchie GA, Hancock G, Robbins PA. Laser-based absorption spectroscopy as a technique for rapid in-line analysis of respired gas concentrations of O2 and CO2. J Appl Physiol (1985) 111: 303–307, 2011. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00119.2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

