FRAGILE-COLCOVID19: A Clinical Trial Based on Early Administration of an Oral Combination of Colchicine and Prednisone in Elderly Patients with COVID-19 in Geriatric Facilities
- PMID: 36173596
- PMCID: PMC9521010
- DOI: 10.1007/s40261-022-01201-2
FRAGILE-COLCOVID19: A Clinical Trial Based on Early Administration of an Oral Combination of Colchicine and Prednisone in Elderly Patients with COVID-19 in Geriatric Facilities
Abstract
Background: Unprotected and fragile elderly people in nursing homes experienced the highest mortality rates during the initial coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Objective: Our aim was to study the role of two oral anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine and prednisone, in elderly patients with COVID-19 in geriatric centers.
Methods: A phase II/III, randomized, controlled, multicenter clinical trial was performed in a geriatric population comparing the efficacy and safety of an oral combination of prednisone (60 mg/day for 3 days) and colchicine (at loading doses of 1-1.5 mg/day for 3 days, followed by 0.5 mg/day for 11 days) with the standard treatment, based on intravenous dexamethasone. Primary endpoints assessed the efficacy in reducing death or the modified endpoint death/therapeutic failure to the study drugs over a 28-day period, while secondary endpoints included safety, laboratory changes, and additional therapies used.
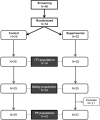
Results: Fifty-four patients (35 female/19 male) were enrolled, 25 (46.3%) of whom were allocated to the experimental arm and 29 (53.7%) to the control arm. At day 28, no differences in deaths were observed. The combination of mortality or therapeutic failure occurred in 12 (45.13%) patients receiving dexamethasone and 6 (28.13%) patients receiving colchicine/prednisone, resulting in a reduction of risk difference (RD) of - 17% (p = 0.17), with an average reduction of 39% (risk ratio [RR] 0.61) in patients receiving colchicine/prednisone (p = 0.25). Control patients received higher amounts of additional glucocorticoids (p = 0.0095) over a longer time frame (p = 0.0003). Colchicine/prednisone significantly reduced ferritin levels at day 14, as well as D-dimer and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels at day 28. Adverse events were similar in both groups.
Conclusions: The combination colchicine/prednisone compared with intravenous dexamethasone has shown a remarkable trend to increase disease survival over a 28-day period in elderly patients requiring oxygen therapy in geriatric centers, without safety issues.
Clinical trial registry: Clinical Trials Registration Number: NCT04492358.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
José Hernández-Rodríguez, Julio Durán-Sanclemente, Sergio Prieto-González, Olga Araújo, Teresa Hospital-Vidal, Georgina Casanovas, Víctor Sapena, José Luis Blanco, and Alfonso López-Soto declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). 2020. Available at : https://www.arcgis.com/apps/dashboards/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6. Accessed 1 June 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

