Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for KCNT1 encephalopathy
- PMID: 36173683
- PMCID: PMC9746904
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.146090
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for KCNT1 encephalopathy
Abstract
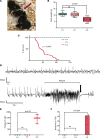
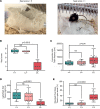
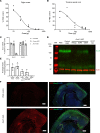
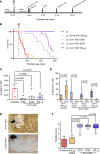
Developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs) are characterized by pharmaco-resistant seizures with concomitant intellectual disability. Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures (EIMFS) is one of the most severe of these syndromes. De novo variants in ion channels, including gain-of-function variants in KCNT1, which encodes for sodium activated potassium channel protein KNa1.1, have been found to play a major role in the etiology of EIMFS. Here, we test a potential precision therapeutic approach in KCNT1-associated DEE using a gene-silencing antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) approach. We generated a mouse model carrying the KCNT1 p.P924L pathogenic variant; only the homozygous animals presented with the frequent, debilitating seizures and developmental compromise that are seen in patients. After a single intracerebroventricular bolus injection of a Kcnt1 gapmer ASO in symptomatic mice at postnatal day 40, seizure frequency was significantly reduced, behavioral abnormalities improved, and overall survival was extended compared with mice treated with a control ASO (nonhybridizing sequence). ASO administration at neonatal age was also well tolerated and effective in controlling seizures and extending the life span of treated animals. The data presented here provide proof of concept for ASO-based gene silencing as a promising therapeutic approach in KCNT1-associated epilepsies.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Gene therapy; Genetics; Mouse models; Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
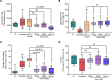
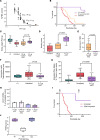
References
-
- Gertler T, et al. KCNT1-Related Epilepsy. In: Adam MP, et al., eds. GeneReviews. University of Washington; 2018. Available from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525917/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

