The use of Trojan-horse drug delivery system in managing periodontitis
- PMID: 36175203
- PMCID: PMC10213762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2022.08.003
The use of Trojan-horse drug delivery system in managing periodontitis
Abstract
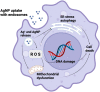
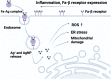
The aim of this review is to evaluate the possibility of delivering a silver-acid complex via a Trojan-horse mechanism for managing periodontits. We theroised that the complex could be an effective treatment option for bacterial inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Searches were conducted using MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science Core Collection, and Google Scholar search engines. We also reviewed several reference lists of the included studies or relevant reviews identified by the search. By using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terminology, a comprehensive search was performed for the following keywords: silver, folic acid, periodontitis, macrophages, Trojan-horse mechanism, toxicity, and targeting. Using the keywords mentioned earlier, we selected 110 articles and after appropriate elimination the review was written based on 37 papers. Accordingly the we noted that silver isons were an effective approach to kill oral pathogens. Secondly the Trojan-horse mechanism. could be used by macrophages (as the Trojan horse) to deliver silver ions in large quantities to the inflammatory focus to kill the periodontopathogens. The Trojan-horse mechanism has never been described in the field of dentistry before. The proposed novel approach using the principle of Trojan Horse delivery of drugs/chemicals could be used to manage oral inflammatory conditions. This method can be used to supplement regular treatments.
Keywords: Drug development; Folic acid; Macrophages; Periodontitis; Silver; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Filoche S, Wong L, Sissons CH. Oral biofilms: emerging concepts in microbial ecology. J Dent Res. 2010;89(1):8–18. - PubMed
-
- Albandar JM, Rams TE. Global epidemiology of periodontal diseases: an overview. Periodontol 2000. 2002;29(1):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Sanz M, Ceriello A, Buysschaert M, et al. Scientific evidence on the links between periodontal diseases and diabetes: consensus report and guidelines of the Joint Workshop on Periodontal Diseases and Diabetes by the International Diabetes Federation and the European Federation of Periodontology. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;137:231–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources