Treatment persistence with aripiprazole once monthly: a 4-year follow-up
- PMID: 36175924
- PMCID: PMC9520898
- DOI: 10.1186/s12991-022-00416-z
Treatment persistence with aripiprazole once monthly: a 4-year follow-up
Abstract
Objectives: Treatment persistence refers to the act of continuing a treatment as prescribed and reflects the patient's or doctor's judgment about efficacy, tolerability, and acceptability. In patients with schizophrenia, antipsychotic persistence is often poor, because of issues such as lack or loss of efficacy, side effects, and poor adherence, which is often related to the degree to which patients find the medication and overall intervention to be helpful, tolerable, fair, reasonable, appropriate, and consistent with expectations of treatment. Despite the poor antipsychotic persistence that has been reported to date in patients with schizophrenia, we previously observed a relatively high (86%) 6 months persistence with aripiprazole once-monthly (AOM) in a group of patients with schizophrenia, treated in the real world Italian clinical practice. The present study explores the longer term persistence with AOM, over a mean follow-up period of 48 months.
Methods: This was a multicenter, retrospective, non-interventional follow-up study, aimed at evaluating the longer term persistence with AOM in a group of patients with schizophrenia who had already shown persistence over a period of at least 6 months. The study included 161 individuals who had participated in our previous study, where 86% of participating individuals had shown persistence with AOM for at least 6 months. Non-persistence was defined as discontinuing the medication for any reason. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of patients who continued AOM were then compared to those of patients who discontinued the medication.
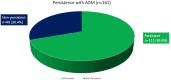
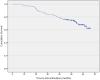
Results: Study subjects were predominantly male (64.4%) and their mean age was 39.7 (SD: 12.24). Treatment persistence with AOM was 69.6% and 112 out of 161 patients were still receiving AOM treatment at the last follow-up visit. The mean duration of AOM treatment until the last recorded observation was 55.87 months (median 56.17, SD6.23) for the 112 persistent patients and 32.23 (median 28.68.SD 15.09) months for the 49 non-persistent individuals. The mean observation period for all patients (persistent and non-persistent) was 48.78 months (median 52.54, SD 14.64). For non-persistent subjects, the observation period ended with the discontinuation of AOM. Subjects treated with AOM at 400 mg presented a 69.6% lower risk of all-cause treatment discontinuation when compared with patients treated with 300 mg (HR: 0.314; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.162-0.608; P = 0.001). The main reasons for discontinuation were lack of efficacy (30.6%), patient/caregiver choice (18.4%), physician's choice (16.3%), non-adherence (12.2%) and inconvenience (6.1%). Only 3 patients (6.1%) discontinued AOM for tolerability issues.
Conclusions: In subjects with schizophrenia, who had already shown a 6 months persistence with AOM, a high number of patients (69.6%) continued to be persistent over a 4-year follow-up period. This may reflect a favourable profile of efficacy, tolerability, and acceptability. Larger and prospective studies are warranted to confirm our observations.
Keywords: Adherence; Aripiprazole; Long acting; Maintenance; Persistence; Retention.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Andrea Fagiolini has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for: Allergan, Angelini, Apsend, Generici DOC, Lundbeck, Italfarmaco, Janssen, Otsuka, Pfizer, Recordati, Roche, Sonofi Aventis, Sunovion; Bernardo Carpiniello has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for: ACRAF Angelini, Janssen Cilag Italia, Lundbeck Italia, Otsuka Italia; Alessandro Cuomo is/has been a consultant and/or a speaker for Angelini, Glaxo Smith Kline, Lundbeck, Janssen, Otsuka, Pfizer, Recordati. Sergio de Filippis has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for: Angelini, Lundbeck, Janssen, Otsuka, Mylan; Jarno Vannucchi is an employee of Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Italy; Claudio Mencacci has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for Lundbeck, Janssen, Italfarmaco; Gino Montagnani is a Lundbeck employee; Giorgio Pigato has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for: Angelini, Lundbeck, Janssen, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Eisai; Antonio Vita has received research grants and/or has been a consultant for, and/or has been a speaker for Angelini, Boheringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly; Fidia, Forum Pharmaceutical; Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck; Otsuka; Recordati; Roche.
Figures


References
-
- Fagiolini A, Aguglia E, Ballerini A, Callista G, Carpiniello B, Clerici M, Corrivetti G, De Fazio P, De Filippis S, De Giorgi S, Favaretto G, Ferri E, Gargiulo G, Giustra MG, La Barbera D, Maina G, Mencacci C, Montagnani G, Panariello A, Pigato G, Tortorella A, Vernacotola L, Vita A. Real-world effectiveness of long acting aripiprazole: treatment persistence and its correlates in the Italian clinical practice. Psychiatry Res. 2019;272:698–706. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

