Acute kidney injury and long-term renal effects of alectinib in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung carcinoma: a case report
- PMID: 36176005
- PMCID: PMC9524124
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-022-03532-2
Acute kidney injury and long-term renal effects of alectinib in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung carcinoma: a case report
Abstract
Background: Targeted therapy with anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor alectinib has become standard therapy for selected patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. Few data are available on the renal effects of alectinib. We report on a case of acute kidney injury in a patient using alectinib for less than 2 weeks and on serum sodium and creatinine during long-term use of alectinib.
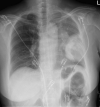
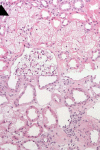
Case presentation: A 70-year-old Asian woman was diagnosed with metastasized non-small cell lung carcinoma (cT4N3M1c, stage IV) with echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 and anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangement and received alectinib, in two daily doses of 600 mg. Eleven days after the initiation of therapy, she was seen at the emergency department with acute kidney injury. Renal biopsy showed lesions in the proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nine days after alectinib cessation, renal function recovered quickly and reintroduction of alectinib in a reduced dose was tolerated, while withholding metformin, enalapril, and naproxen. In seven other patients, data on estimated glomerular filtration rate showed decreased kidney function at 3 months with stabilization at 6 months. Serum sodium at 3 months increased during alectinib treatment and increased further at 6 months.
Conclusions: Our data suggest direct or indirect toxic (proximal) tubulopathy due to alectinib with a good prognosis after cessation. Adverse acute renal effects of alectinib may be prevented by avoiding other medication influencing renal hemodynamics, in particular nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Without these co-medications, alectinib could be reintroduced in our patient.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Alectinib; Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Case report; Tubular toxicity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brosnan EM, Weickhardt AJ, Lu X, Maxon DA, Barón AE, Chonchol M, et al. Drug-induced reduction in estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated with the ALK inhibitor crizotinib. Cancer. 2014;120:664–674. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28478. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

