Progress towards the UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets among persons aged 50 and older living with HIV in 13 African countries
- PMID: 36176030
- PMCID: PMC9522983
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.26005
Progress towards the UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets among persons aged 50 and older living with HIV in 13 African countries
Abstract
Introduction: Achieving optimal HIV outcomes, as measured by global 90-90-90 targets, that is awareness of HIV-positive status, receipt of antiretroviral (ARV) therapy among aware and viral load (VL) suppression among those on ARVs, respectively, is critical. However, few data from sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) are available on older people (50+) living with HIV (OPLWH). We examined 90-90-90 progress by age, 15-49 (as a comparison) and 50+ years, with further analyses among 50+ (55-59, 60-64, 65+ vs. 50-54), in 13 countries (Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe).
Methods: Using data from nationally representative Population-based HIV Impact Assessments, conducted between 2015and 2019, participants from randomly selected households provided demographic and clinical information and whole blood specimens for HIV serology, VL and ARV testing. Survey weighted outcomes were estimated for 90-90-90 targets. Country-specific Poisson regression models examined 90-90-90 variation among OPLWH age strata.
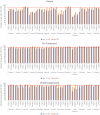
Results: Analyses included 24,826 HIV-positive individuals (15-49 years: 20,170; 50+ years: 4656). The first, second and third 90 outcomes were achieved in 1, 10 and 5 countries, respectively, by those aged 15-49, while OPLWH achieved outcomes in 3, 13 and 12 countries, respectively. Among those aged 15-49, women were more likely to achieve 90-90-90 targets than men; however, among OPLWH, men were more likely to achieve first and third 90 targets than women, with second 90 achievement being equivalent. Country-specific 90-90-90 regression models among OPLWH demonstrated minimal variation by age stratum across 13 countries. Among OLPWH, no first 90 target differences were noted by age strata; three countries varied in the second 90 by older age strata but not in a consistent direction; one country showed higher achievement of the third 90 in an older age stratum.
Conclusions: While OPLWH in these 13 countries were slightly more likely than younger people to be aware of their HIV-positive status (first 90), this target was not achieved in most countries. However, OPLWH achieved treatment (second 90) and VL suppression (third 90) targets in more countries than PLWH <50. Findings support expanded HIV testing, prevention and treatment services to meet ongoing OPLWH health needs in SSA.
Keywords: HIV epidemiology; HIV testing; PHIA; UNAIDS goals; ageing; older PLHIV.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare for any authors.
Figures
References
-
- Joint United Nationas Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) . 90‐90‐90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS); 2014.
-
- UNAIDS . World AIDS day report 2020: prevailing against pandemics by putting people at the centre. 2020. [cited 2022 Feb 17] https://aidstargets2025.unaids.org/assets/images/prevailing‐against‐pand...
-
- UNAIDS . Global AIDS strategy 2021–2016. End inequalities. End AIDS. 2021. [cited 2022 Feb 17] https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/global‐AIDS‐strat...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

