The effect of neurologic music therapy in patients with cerebral palsy: A systematic narrative review
- PMID: 36176557
- PMCID: PMC9514322
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.852277
The effect of neurologic music therapy in patients with cerebral palsy: A systematic narrative review
Abstract
Background: Cerebral palsy (CP) is one of the most common causes of disability in children. It is characterized by impairment in motor function and coordination and difficulties in performing daily life activities. Previous research supports that neurologic music therapy (NMT) was effective in improving motor function, cognition, and emotional wellbeing in patients with various neurologic disorders. However, the benefit of NMT in patients with CP have not yet been thoroughly investigated. The aim of this review was to investigate the potential effect of NMT motor rehabilitation techniques for patients.
Materials and methods: We searched articles published up to May 24, 2022 in PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane library, Web of science, and Ovid MEDLINEdatabases. We included studies that investigated the effect of NMT in patients with CP.
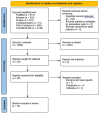
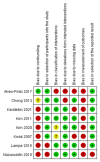
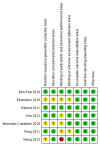
Results: After search, 4,117 articles were identified using the search terms. After reading the titles and abstracts, 4,089 articles that did not meet our inclusion criteria were excluded. The remaining 28 articles which were assessed for eligibility. Finally, 15 studies were included in this systematic review. Among 15 studies that investigated the effect of NMT on patients with CP, 7 studies were on rhythmic auditory stimulation (RAS), 6 studies were on therapeutic instrumental music performance (TIMP), and 2 studies were on patterned sensory enhancement (PSE).
Conclusions: Various techniques of NMT brings beneficial effects for gross and fine motor improvements in patients with CP. NMT techniques, such as RAS, TIMP, and PSE, may be a potential alternative rehabilitation strategy to enhance gross and fine motor skills for patients with CP.
Keywords: cerebral palsy; motor; music; music therapy; neurologic music therapy; rehabilitation.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Suh, Kwon and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurologic Music Therapy Improves Participation in Children With Severe Cerebral Palsy.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 9;13:795533. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.795533. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35356462 Free PMC article.
-
A home-based program using patterned sensory enhancement improves resistance exercise effects for children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2013 Oct;27(8):684-94. doi: 10.1177/1545968313491001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2013. PMID: 23757295 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized controlled trial of neurologic music therapy in Parkinson's disease: research rehabilitation protocols for mechanistic and clinical investigations.Trials. 2021 Aug 28;22(1):577. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05560-7. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34454592 Free PMC article.
-
Neurologic Music Therapy in Geriatric Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;10(11):2187. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10112187. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurologic music therapy for non-fluent aphasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2024 May 23;15:1395312. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1395312. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38846040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Motor-Sensory Learning in Children with Disabilities: Does Piano Practice Help?Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;12(3):335. doi: 10.3390/children12030335. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150617 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of music-based game approaches with wearable devices for hand neurorehabilitation: a narrative review.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024 May 29;21(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12984-024-01379-w. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38811987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Music Therapy on Neurodevelopment of Preterm Infants and Functional Improvement in Children with Neurological Deficits.Pediatr Rep. 2025 Mar 28;17(2):41. doi: 10.3390/pediatric17020041. Pediatr Rep. 2025. PMID: 40278521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musicians and researchers: two creative professions striving to improve heart health through music.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 10;11:1536829. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1536829. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39866798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vinolo-Gil MJ, Casado-Fernández E, Perez-Cabezas V, Gonzalez-Medina G, Martín-Vega FJ, Martín-Valero R. Effects of the combination of music therapy and physiotherapy in the improvement of motor function in cerebral palsy: a challenge for research. Children. (2021) 8:868. 10.3390/children8100868 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoon AH Jr, Stashinko EE, Nagae LM, Lin DD, Keller J, Bastian A, et al. . Sensory and motor deficits in children with cerebral palsy born preterm correlate with diffusion tensor imaging abnormalities in thalamocortical pathways. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2009) 51:697–704. 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03306.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous