Molecular glues modulate protein functions by inducing protein aggregation: A promising therapeutic strategy of small molecules for disease treatment
- PMID: 36176907
- PMCID: PMC9513498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.03.019
Molecular glues modulate protein functions by inducing protein aggregation: A promising therapeutic strategy of small molecules for disease treatment
Abstract
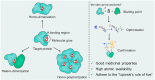
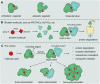
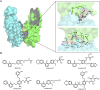
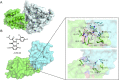
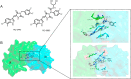
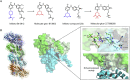
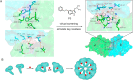
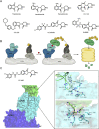
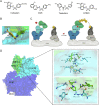
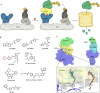
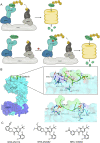
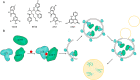
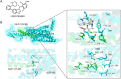
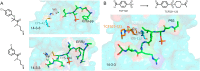
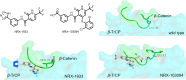
Molecular glues can specifically induce aggregation between two or more proteins to modulate biological functions. In recent years, molecular glues have been widely used as protein degraders. In addition, however, molecular glues play a variety of vital roles, such as complex stabilization, interactome modulation and transporter inhibition, enabling challenging therapeutic targets to be druggable and offering an exciting novel approach for drug discovery. Since most molecular glues are identified serendipitously, exploration of their systematic discovery and rational design are important. In this review, representative examples of molecular glues with various physiological functions are divided into those mediating homo-dimerization, homo-polymerization and hetero-dimerization according to their aggregation modes, and we attempt to elucidate their mechanisms of action. In particular, we aim to highlight some biochemical techniques typically exploited within these representative studies and classify them in terms of three stages of molecular glue development: starting point, optimization and identification.
Keywords: Dimerization; Molecular glue; Polymerization; Protein–protein interaction; Small molecule.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Roberts N.A., Martin J.A., Kinchington D., Broadhurst A.V., Craig J.C., Duncan I.B., et al. Rational design of peptide-based HIV proteinase inhibitors. Science. 1990;248:358–361. - PubMed
-
- Erickson J., Neidhart D.J., VanDrie J., Kempf D.J., Wang X.C., Norbeck D.W., et al. Design, activity, and 2.8 Å crystal structure of a C2 symmetric inhibitor complexed to HIV-1 protease. Science. 1990;249:527–533. - PubMed
-
- Dorsey B.D., Levin R.B., McDaniel S.L., Vacca J.P., Guare J.P., Darke P.L., et al. L-735,524: the design of a potent and orally bioavailable HIV protease inhibitor. J Med Chem. 1994;37:3443–3451. - PubMed
-
- Anderson A.C. The process of structure-based drug design. Chem Biol. 2003;10:787–797. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

