Lenvatinib- and vadimezan-loaded synthetic high-density lipoprotein for combinational immunochemotherapy of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 36176911
- PMCID: PMC9513558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.021
Lenvatinib- and vadimezan-loaded synthetic high-density lipoprotein for combinational immunochemotherapy of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
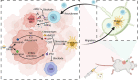
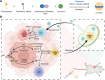
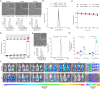
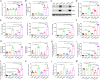
Metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive type of breast cancer. Combination of systemic chemotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade is effective but of limited benefit due to insufficient intratumoral infiltration of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and the accumulation of immunosuppressive cells. Herein, we designed a lenvatinib- and vadimezan-loaded synthetic high-density lipoprotein (LV-sHDL) for combinational immunochemotherapy of metastatic TNBC. The LV-sHDL targeted scavenger receptor class B type 1-overexpressing 4T1 cells in the tumor after intravenous injection. The multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) lenvatinib induced immunogenic cell death of the cancer cells, and the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist vadimezan triggered local inflammation to facilitate dendritic cell maturation and antitumor macrophage differentiation, which synergistically improved the intratumoral infiltration of total and active CTLs by 33- and 13-fold, respectively. LV-sHDL inhibited the growth of orthotopic 4T1 tumors, reduced pulmonary metastasis, and prolonged the survival of animals. The efficacy could be further improved when LV-sHDL was used in combination with antibody against programmed cell death ligand 1. This study highlights the combination use of multitargeted TKI and STING agonist a promising treatment for metastatic TNBC.
Keywords: Combination therapy; High-density lipoprotein; Immune checkpoint blockade; Immunotherapy; Lenvatinib; Metastasis; Triple-negative breast cancer; Vadimezan.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanodroplet-enhanced sonodynamic therapy potentiates immune checkpoint blockade for systemic suppression of triple-negative breast cancer.Acta Biomater. 2023 Mar 1;158:547-559. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.12.023. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36539109
-
Camptothesome Potentiates PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Improved Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Immunochemotherapy.Mol Pharm. 2022 Dec 5;19(12):4665-4674. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00701. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Mol Pharm. 2022. PMID: 36413426 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine-modulating synthetic high-density lipoprotein for chemoimmunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer.J Control Release. 2024 Mar;367:637-648. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.064. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38295994
-
Platinum-based chemotherapy in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: preclinical and clinical studies and mechanism of action.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Feb;18(2):187-203. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2021.1825376. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 32954856 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors for triple-negative breast cancer: From immunological mechanisms to clinical evidence.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Sep;98:107876. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107876. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34146865 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Aug 7;4(4):e339. doi: 10.1002/mco2.339. eCollection 2023 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37560754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated spatial multi-omics profiling of Fusobacterium nucleatum in breast cancer unveils its role in tumour microenvironment modulation and cancer progression.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70273. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70273. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40070022 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical conjugation mitigates immunotoxicity of chemotherapy via reducing receptor-mediated drug leakage from lipid nanoparticles.Sci Adv. 2024 Jun 7;10(23):eadk9996. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk9996. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38838152 Free PMC article.
-
Mannose-functionalization of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein nanoparticles improves payload delivery and enhances M2-to-M1 phenotype reprogramming of RAW 264.7 macrophages polarized by B16-F10 melanoma cells.Front Drug Deliv. 2023 Oct 24;3:1281066. doi: 10.3389/fddev.2023.1281066. eCollection 2023. Front Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 40838054 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules against Metastatic Tumors: Concrete Perspectives and Shattered Dreams.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 18;15(16):4173. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164173. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Waks A.G., Winer E.P. Breast cancer treatment: a review. JAMA. 2019;321:288–300. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Gradishar W.J., Tjulandin S., Davidson N., Shaw H., Desai N., Bhar P., et al. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7794–7803. - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L., Buqué A., Kepp O., Zitvogel L., Kroemer G. Immunological effects of conventional chemotherapy and targeted anticancer agents. Cancer Cell. 2015;28:690–714. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

