Effects of Sports Functional Food on Physical Function of Athletes under Ultrasound Observation
- PMID: 36177154
- PMCID: PMC9492428
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7769653
Effects of Sports Functional Food on Physical Function of Athletes under Ultrasound Observation
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Sports Functional Food on Physical Function of Athletes under Ultrasound Observation.Scanning. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9760176. doi: 10.1155/2023/9760176. eCollection 2023. Scanning. 2023. PMID: 37476097 Free PMC article.
Abstract
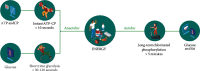
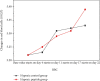
In order to improve the physical function of athletes under hypoxic training, the authors propose to observe the effect of functional food with active ingredients of polypeptide polyamines in deer antler on the physical function of athletes under ultrasound observation. According to the characteristics of physiological changes during hypoxic training, functional foods containing the active ingredients of polypeptide polyamines in deer antler were selected and given to athletes under simulated hypoxic training, observe the changes of red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (Hct), blood lactic acid, free radical metabolism and immune function of athletes, and musculoskeletal under ultrasound observation, discuss how to improve the physical function and athletic ability of athletes under hypoxic training. Experimental results show that athletes after 6 weeks of hypoxic training, red blood cells and hemoglobin were significantly increased, there was a significant difference compared to the control group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). After 6 weeks of hypoxic training, hemoglobin increased by 10.1%, a 5.6 percentage point increase compared to the control group. Conclusion. The antler peptides used by the authors can enhance the effect of hypoxic training.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of six weeks of sub-plateau cold environment training on physical functioning and athletic ability in elite parallel giant slalom snowboard athletes.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 26;11:e14770. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14770. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36721778 Free PMC article.
-
A three-week traditional altitude training increases hemoglobin mass and red cell volume in elite biathlon athletes.Int J Sports Med. 2005 Jun;26(5):350-5. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-821052. Int J Sports Med. 2005. PMID: 15895317 Clinical Trial.
-
Hematological indices and iron status in athletes of various sports and performances.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002 May;34(5):869-75. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200205000-00022. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002. PMID: 11984308
-
Current trends in altitude training.Sports Med. 2001;31(4):249-65. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200131040-00002. Sports Med. 2001. PMID: 11310547 Review.
-
The Effect of Natural or Simulated Altitude Training on High-Intensity Intermittent Running Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2018 Feb;48(2):431-446. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0809-9. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29129021 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Effects of Sports Functional Food on Physical Function of Athletes under Ultrasound Observation.Scanning. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9760176. doi: 10.1155/2023/9760176. eCollection 2023. Scanning. 2023. PMID: 37476097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yokosaka T., Kuroki S., Nishida S. Describing the sensation of the 'velvet hand illusion' in terms of common materials. IEEE Transactions on Haptics . 2021;14:680–685. - PubMed
-
- Mhb A., Aj A., Eb A., Fk B., Ne C. Both high-intensity interval training and low-intensity endurance training decrease intrahepatic lipid deposits via alterations of the expression of hif-1α, hig2 in a murine model of non alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) Science & Sports . 2021;36(2):120–128. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2020.3046376. - DOI
-
- Lane S. M., Cornwell T. O., Briffa M. The angle of attack: rapping technique predicts skill in hermit crab contests. Animal Behaviour . 2022;187:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2022.02.017. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources