Faculty perspectives of small group teaching experience in medical school in Tamil Nadu
- PMID: 36177410
- PMCID: PMC9514274
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_8_22
Faculty perspectives of small group teaching experience in medical school in Tamil Nadu
Abstract
Background: The small group teaching (SGT) is gaining popularity in medical education since it improves the student's thinking capacity and aids knowledge retention. Several studies have been conducted to analyze students' attitudes regarding SGT. Faculty, on the other hand, have mixed perception about SGT methodology. Therefore, the main objective of this study was to explore medical faculties' perceptions of SGT effectiveness in the medical curriculum.
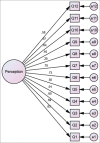
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional, descriptive survey was conducted among 50 medical college teachers. We have developed set of 12 questionnaires to assess the perception of teachers on SGT methods. Content validation of the survey questionnaire was done by Lawshe method, and Cronbach's alpha was calculated for estimating the internal consistency. Teacher's perception responses were presented as proportion and percentage. We performed principal component analysis, structural equation modelling, Chi-squared test (χ2/df), goodness-of-fit index (GFI), adjusted GFI, comparative fit index, and root mean square error of approximation.
Results: The validation resulted in the 12 items model indicated superior goodness of fit for sample data. All the extracted factors had good internal consistency of >0.9. Majority of the teachers strongly agreed that the SGT method enhances the student intrinsic motivation (n = 42, 84%), self-confidence (n = 40, 80%) self-directed learning (n = 35, 70%), and student teacher interaction (n = 38, 76%).
Conclusion: Teaching faculties' perception reflected that SGT is an effective method to impart knowledge to the students and also helps in improving their understanding of their subject. It helps in developing intrinsic motivation to do self-learning in the students. It also helps in developing good peer interaction and improves the communication skills.
Keywords: Education; medical teachers; perception; teaching methods.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bennett J, Hogarth S, Lubben F, Campbell B, Robinson A. Talking science: The research evidence on the use of small group discussions in science teaching. Int J Sci Educ. 2010;32:69–95.
-
- Rezaeian M. A review on different roles of the participants in a small teaching group. J Rafsanjan Univ Med Sci. 2021;19:1225–30.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous