Twenty-year medication use trends in first-episode bipolar disorder
- PMID: 36177718
- PMCID: PMC9828455
- DOI: 10.1111/acps.13504
Twenty-year medication use trends in first-episode bipolar disorder
Abstract
Objectives: To study the medication use patterns in patients newly diagnosed with bipolar disorder (BD) in Finland during the past 20 years.
Methods: All persons diagnosed with BD between 1996 and 2018, aged 16-65 years, with no previous BD diagnosis were identified from nationwide Finnish registers (N = 26,395). The point prevalences of medication use were observed up until 5 years after the first diagnosis. Five sub-cohorts according to calendar year of first diagnosis were also formed and the prevalence of medication use was compared between sub-cohorts 3 months after diagnosis. Medication data were modeled with the PRE2DUP-method using dispensing data.
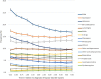
Results: The prevalence of overall medication use declined during the 5-year follow-up period in the total cohort. The highest prevalence of use was seen 3 months after diagnosis for the three main medication classes-antidepressants (40.8%), antipsychotics (30.8%) and mood stabilizers (29.2%). The prevalence of lithium use varied between 5.9% and 6.5% during the 5 years in the total cohort, and the lowest prevalence of use at 3 months was seen in sub-cohort diagnosed in 2016-2018 (4.1%) versus 12.1% in 1996-2000 sub-cohort. The prevalence of benzodiazepine use was between 12.4% and 13.5% and the prevalence of Z-drugs was between 7.3% and 7.9% during the 5 years. The prevalence of long-acting injectable antipsychotic (LAI) use was the highest in patients diagnosed in 2016-2018, although still only 0.8%.
Conclusions: (i) The use of antidepressants is too prevalent, (ii) the use of lithium is declining and needs to be increased, and (iii) LAIs are markedly underutilized as compared to their oral counterparts.
Keywords: antipsychotics; bipolar disorder; medication trends; mood stablizers; pharmacoepidemiology.
© 2022 The Authors. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Jari Tiihonen, Heidi Taipale and Antti Tanskanen have participated in research projects funded by grants from Janssen‐Cilag and Eli Lilly to their employing institution. Heidi Taipale reports personal fees from Janssen‐Cilag and Otsuka. Jari Tiihonen reports personal fees from Eli Lilly, Evidera, Janssen‐Cilag, Lundbeck, Mediuutiset, Otsuka, Sidera, and Suvovion; and is a consultant to Orion and HLS Therapeutics. Markku Lähteenvuo is a board member of Genomi Solutions Ltd., Nursie Health Ltd., and Springflux Ltd. has received honoraria from Sunovion, Orion Pharma, Lundbeck, Otsuka Pharma, Recordati, Janssen and Janssen‐Cilag and research funding from the Finnish Cultural Foundation and the Emil Aaltonen Foundation.
Figures


Comment in
-
The lithium paradox: declining prescription of the gold standard treatment for bipolar disorder.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2023 Mar;147(3):314-315. doi: 10.1111/acps.13525. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2023. PMID: 36527204 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

