Underuse of lifestyle recommendations in hypertension management in France: The Esteban study
- PMID: 36177966
- PMCID: PMC9581092
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14576
Underuse of lifestyle recommendations in hypertension management in France: The Esteban study
Abstract
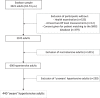
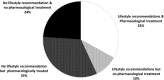
Lifestyle recommendations are first-line elements in the management of arterial hypertension. This cross-sectional study aimed to analyze the level to which lifestyle recommendations are used in hypertension management in France, using data from the Esteban study, which was implemented by Santé Publique France, France's public health agency, from 2014 to 2016 on a representative sample of the French population. The study sample comprised 440 adult Esteban participants who were aware they had hypertension and were aged 18-74 years old. The main outcomes were the proportion of participants who received lifestyle recommendations in their hypertension management plan, and the proportion of recommendations according to the three following dimensions: physical activity, weight loss, and changes in diet. Over half (57.0%) of the 440 participants declared they did not receive lifestyle recommendations as part of their hypertension management plan in the year preceding the study. Of these, 39.0% did not receive pharmacological treatment either. Physical activity was recommended to 31.8% of sedentary participants and weight loss to 26.8% of participants with overweight or obesity. One-fifth of the study sample (20.1%) received dietary recommendations. Of these, 69% and 10.7% were advised to limit their salt and alcohol intake, respectively. Lifestyle interventions are too rarely recommended in hypertension management plans in France. Adherence to lifestyle recommendations needs in-depth discussion not only at the time of diagnosis but also throughout follow-up.
Keywords: healthy diet; hypertension management; lifestyle recommendations; physical activity; weight loss.
© 2022 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Juliette VAY‐DEMOUY reports, outside the submitted work, financial support from Boston Scientific SAS and AstraZeneca. Jacques BLACHER reports, outside the submitted work, personal fees from Abbott, Bayer, Bottu, Ferring, Steripharma, Kantar, Teriak, personal fees and non‐financial support from Pfizer, Quantum Genomics, Sanofi and Servier. Pauline NEUDORFF, Valérie OLIE, Clémence GRAVE and Amélie GABET declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patterns of hypertension management in France in 2015: The ESTEBAN survey.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020 Apr;22(4):663-672. doi: 10.1111/jch.13834. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2020. PMID: 32092238 Free PMC article.
-
Patient recall of receiving lifestyle advice for overweight and hypertension from their General Practitioner.BMC Fam Pract. 2010 Feb 1;11:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-11-8. BMC Fam Pract. 2010. PMID: 20113530 Free PMC article.
-
[Management of severe hypertension in France in 1999 and 2000: intermediate results of a health insurance intervention program].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002 Jul-Aug;95(7-8):687-94. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002. PMID: 12365081 French.
-
The 2010 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 2 - therapy.Can J Cardiol. 2010 May;26(5):249-58. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(10)70379-2. Can J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20485689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 2009 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part 2--therapy.Can J Cardiol. 2009 May;25(5):287-98. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(09)70492-1. Can J Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19417859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-sectional associations between healthy and unhealthy plant-based diets and metabolic syndrome in three distinct French populations: a meta-analysis.Br J Nutr. 2025 Mar 3;133(7):1-17. doi: 10.1017/S0007114525000376. Online ahead of print. Br J Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40026144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. J Hypertens. 2020;38(6):982‐1004. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 Practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology: ESH/ESC task force for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36(12):2284‐2309. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R. Practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013(31):1925‐1938. - PubMed
-
- Blacher J, Halimi JM, Hanon O, et al. Management of arterial hypertension in adults: 2013 guidelines of the French society of arterial hypertension. Presse Med. 2013;42(5):819‐825. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical