The emerging significance of splicing in vertebrate development
- PMID: 36178052
- PMCID: PMC9641660
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.200373
The emerging significance of splicing in vertebrate development
Abstract
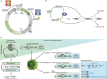
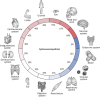
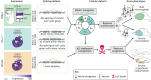
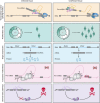
Splicing is a crucial regulatory node of gene expression that has been leveraged to expand the proteome from a limited number of genes. Indeed, the vast increase in intron number that accompanied vertebrate emergence might have aided the evolution of developmental and organismal complexity. Here, we review how animal models for core spliceosome components have provided insights into the role of splicing in vertebrate development, with a specific focus on neuronal, neural crest and skeletal development. To this end, we also discuss relevant spliceosomopathies, which are developmental disorders linked to mutations in spliceosome subunits. Finally, we discuss potential mechanisms that could underlie the tissue-specific phenotypes often observed upon spliceosome inhibition and identify gaps in our knowledge that, we hope, will inspire further research.
Keywords: Introns; Spliceosome; Spliceosomopathies; Splicing; Tissue-specific phenotypes; Vertebrate development.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alam, S. S., Kumar, S., Beauchamp, M.-C., Bareke, E., Boucher, A., Nzirorera, N., Dong, Y., Padilla, R., Zhang, S. J., Majewski, J. et al. (2022). Snrpb is required in murine neural crest cells for proper splicing and craniofacial morphogenesis. Dis. Models Mech. 15, dmm049544. 10.1242/dmm.049544 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balestra, D., Giorgio, D., Bizzotto, M., Fazzari, M., Ben Zeev, B., Pinotti, M., Landsberger, N. and Frasca, A. (2019). Splicing mutations impairing CDKL5 expression and activity can be efficiently rescued by U1snRNA-based therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, E4130. 10.3390/ijms20174130 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

