Clinical outcomes and structural remodelling after ablation of atrial fibrillation in heart failure with mildly reduced or mid-range ejection fraction
- PMID: 36178105
- PMCID: PMC9871718
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14178
Clinical outcomes and structural remodelling after ablation of atrial fibrillation in heart failure with mildly reduced or mid-range ejection fraction
Abstract
Aims: The efficacy of catheter ablation (CA) on clinical outcomes and cardiac structural remodelling in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients with HF with mildly reduced or mid-range ejection fraction (HFmrEF) remains unclear. We aimed to compare the efficacy of CA with medical therapy (MT) in AF patients with HFmrEF.
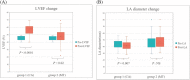
Methods and results: We retrospectively screened a total of 36 879 patients with AF between 2005 and 2020. Patients who were initially diagnosed with echocardiography-proved HFmrEF and had follow-up echocardiography were enrolled. After applying propensity score matching in a 1:1 ratio, 72 patients treated by CA (Group 1) and 72 patients receiving MT (Group 2) were taken into further analysis. The co-morbidities were similar between the two groups, except for hyperlipidaemia. After a mean follow-up duration of 58.9 ± 42.6 months, Group 1 had a lower HF hospitalization and all-cause mortality compared with Group 2 (hazard ratio (HR), 0.089 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.011-0.747]; P = 0.026 and HR, 0.121 [95% CI, 0.016-0.894]; P = 0.038, respectively). As for cardiac structural remodelling, the Group 1 had a better improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and a more decreased left atrium (LA) diameter than Group 2 (+25.0% ± 18.0% vs. +6.2% ± 21.6%, P = <0.0001 and -1.6 ± 4.7 mm vs. +1.5 ± 8.2 mm, P = 0.008, respectively).
Conclusions: In patients with HFmrEF and AF, CA of AF could reduce both HF hospitalization and all-cause mortality as compared with those with MT. A significant improvement in LVEF and decrease in LA diameter were also observed in the CA group. Early rhythm control with CA should be taken into consideration in patients with HFmrEF and AF.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial fibrillation; Heart failure; Mildly reduced ejection fraction; Outcome.
© 2022 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognosis and treatment strategies for atrial fibrillation in heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024 Aug 22;31(11):1372-1384. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae185. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38825871
-
Cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Feb;10(1):518-531. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14212. Epub 2022 Nov 3. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36325978 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Heart Failure Subtypes.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2024 Sep;17(9):e012926. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.124.012926. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2024. PMID: 39193716
-
Improved survival in patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure undergoing catheter ablation compared to medical treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022 Nov;33(11):2356-2366. doi: 10.1111/jce.15622. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35842804
-
A comprehensive meta-analysis comparing radiofrequency ablation versus pharmacological therapy for the treatment of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure.Int J Cardiol. 2023 Apr 15;377:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.01.070. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Int J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36709925
Cited by
-
Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence Post-Ablation Across Heart Failure Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Cardiol Res. 2025 Feb;16(1):33-43. doi: 10.14740/cr2020. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Cardiol Res. 2025. PMID: 39897444 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial fibrillation ablation in heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction: Is it time to open the champagne?Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2023 Sep-Oct;23(5):142-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2023.08.004. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2023. PMID: 37652619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sacubitril-Valsartan Lowers Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence and Left Atrial Volume Post-catheter Ablation: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2025 Mar;25(2):157-167. doi: 10.1007/s40256-024-00691-z. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39470948
-
Understanding Transient Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Reduction During Atrial Fibrillation With Artificial Intelligence.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 May 20;14(10):e040641. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.040641. Epub 2025 May 13. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40357662 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Catheter Ablation in Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction, Stroke, Quality of Life, All-Cause Mortality, Sinus Rhythm Maintenance, and Hospitalization Rates as Compared to Medical Therapy.Cureus. 2023 Aug 12;15(8):e43372. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43372. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37700942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, ESC Scientific Document Group . 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016; 18: 891–975. - PubMed
-
- Chioncel O, Lainscak M, Seferovic PM, Anker SD, Crespo‐Leiro MG, Harjola VP, Parissis J, Laroche C, Piepoli MF, Fonseca C, Mebazaa A, Lund L, Ambrosio GA, Coats AJ, Ferrari R, Ruschitzka F, Maggioni AP, Filippatos G. Epidemiology and one‐year outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved, mid‐range and reduced ejection fraction: An analysis of the ESC heart failure long‐term registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017; 19: 1574–1585. - PubMed
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Crespo‐Leiro MG, Farmakis D, Gilard M, Heymans S, Hoes AW, Jaarsma T, Jankowska EA, Lainscak M, Lam CSP, Lyon AR, McMurray JJV, Mebazaa A, Mindham R, Muneretto C, Francesco Piepoli M, Price S, Rosano GMC, Ruschitzka F, Kathrine Skibelund A, ESC Scientific Document Group . 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021; 42: 3599–3726. - PubMed
-
- Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Trends in prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355: 251–259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 111003/SZU-YUAN RESEARCH FOUNDATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
- 110008/SZU-YUAN RESEARCH FOUNDATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
- 109024/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 108010/SZU-YUAN RESEARCH FOUNDATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
- "Yin Yen-Liang Foundation Development and Construction Plan" of the College of Medicine, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University
- MOST106-2314-B-010-035-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- 109-2314-B-010-063/Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- 110-2314-B-A49A-542/Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- 111-2314-B-A49-007-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- V111C-075/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V110C-004/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V109C-008/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V108C-055/Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- 109024/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

