Cytokine production by human B cells: role in health and autoimmune disease
- PMID: 36179248
- PMCID: PMC9985175
- DOI: 10.1093/cei/uxac090
Cytokine production by human B cells: role in health and autoimmune disease
Abstract
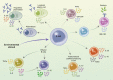
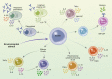
B cells are classically considered solely as antibody-producing cells driving humoral immune responses to foreign antigens in infections and vaccinations as well as self-antigens in pathological settings such as autoimmunity. However, it has now become clear that B cells can also secrete a vast array of cytokines, which influence both pro- and anti-inflammatory immune responses. Indeed, similarly to T cells, there is significant heterogeneity in cytokine-driven responses by B cells, ranging from the production of pro-inflammatory effector cytokines such as IL-6, through to the release of immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-10. In this review, focusing on human B cells, we summarize the key findings that have revealed that cytokine-producing B cell subsets have critical functions in healthy immune responses and contribute to the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: B cells; autoimmunity; cytokine; inflammation.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

