Small-molecule screening identifies Syk kinase inhibition and rutaecarpine as modulators of macrophage training and SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 36179680
- PMCID: PMC9474420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111441
Small-molecule screening identifies Syk kinase inhibition and rutaecarpine as modulators of macrophage training and SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
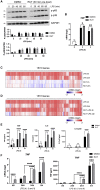
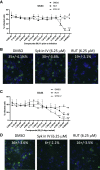
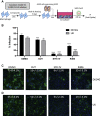
Biologically active small molecules can impart modulatory effects, in some cases providing extended long-term memory. In a screen of biologically active small molecules for regulators of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induction, we identify several compounds with the ability to induce training effects on human macrophages. Rutaecarpine shows acute and long-term modulation, enhancing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and relieving LPS tolerance in human macrophages. Rutaecarpine inhibits β-glucan-induced H3K4Me3 marks at the promoters of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, highlighting the potential of this molecule to modulate chromosomal topology. Syk kinase inhibitor (SYKi IV), another screen hit, promotes an enhanced response to LPS similar to that previously reported for β-glucan-induced training. Macrophages trained with SYKi IV show a high degree of resistance to influenza A, multiple variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and OC43 coronavirus infection, highlighting a potential application of this molecule and other SYKis as prophylactic treatments for viral susceptibility.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; LPS tolerance; NFAT-2; SARS-CoV-2; Syk inhibition; innate immune training; rutaecarpine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Aaby P., Jensen H., Samb B., Cisse B., Sodemann M., Jakobsen M., Poulsen A., Rodrigues A., Lisse I.M., Simondon F., Whittle H. Differences in female-male mortality after high-titre measles vaccine and association with subsequent vaccination with diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis and inactivated poliovirus: reanalysis of West African studies. Lancet. 2003;361:2183–2188. - PubMed
-
- Arron J.R., Winslow M.M., Polleri A., Chang C.P., Wu H., Gao X., Neilson J.R., Chen L., Heit J.J., Kim S.K., et al. NFAT dysregulation by increased dosage of DSCR1 and DYRK1A on chromosome 21. Nature. 2006;441:595–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

